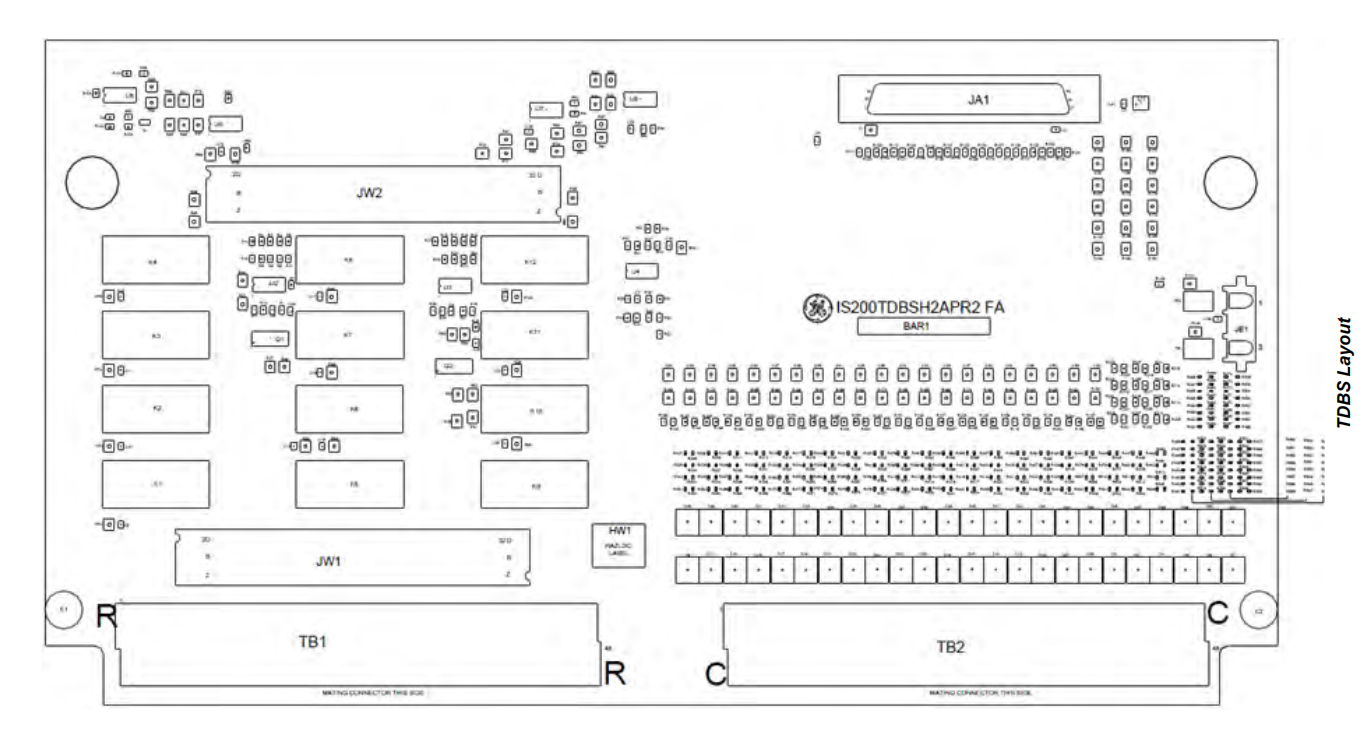
The IS200TDBSH2A is a Simplex Discrete Input/Output Terminal Board designed by General Electric (GE) for the Mark VIe and Mark VIeS control systems. It is a member of the TDBS series, specifically intended for applications requiring a nominal 24V DC wetting voltage. This terminal board acts as an interface bridge between the PDIO I/O module and field devices, primarily responsible for receiving field discrete signals (such as contacts from buttons, limit switches) and driving field loads (such as relays, solenoid valves, indicator lights). Its design supports DIN-rail or flat mounting, featuring high reliability, ease of maintenance, and flexible expansion. It is widely used in industrial automation and control, especially in critical process control applications like gas and steam turbines.
Core Functional Description
The core functions of the IS200TDBSH2A are clearly divided into two main parts: Discrete Inputs and Relay Outputs.
24-Channel Discrete Input
Noise Suppression: Built-in noise suppression effectively protects against surge spikes and high-frequency noise, ensuring signal stability and accuracy in harsh industrial electromagnetic environments.
Hardware Filtering: Features a 4-millisecond hardware filter to eliminate transient interference like contact bounce, preventing false triggering.
Input Type: Accepts 24 "dry contact" signals, i.e., passive switch contacts provided by field devices.
Wetting Voltage: To detect the state of the contacts (open or closed), the terminal board requires an external wetting voltage. The IS200TDBSH2A supports a nominal wetting voltage of 24V DC, with an acceptable range of 16 to 32V DC. This voltage is floating, enhancing noise immunity.
Signal Conditioning: Each input channel is equipped with advanced signal conditioning circuits.
Input Current: The input current is limited by internal resistors. The typical current is 2.5mA for the first 21 circuits and 10mA for the last three circuits (22-24). This design helps reduce power consumption and improve safety.
Wiring: The 24 inputs are connected via the lower 48-point pluggable terminal block (TB2). Each input group uses two terminals (e.g., Wet 1 and In 1), ensuring clear wiring.
12-Channel Relay Output
Relay Type: Provides 12 Form-C (break-before-make) relay contacts. Each relay provides three output terminals: Normally Closed (NC), Common (COM), and Normally Open (NO). This structure offers great flexibility for control logic (able to choose to make or break a circuit).
Load Capacity: The relay contacts use silver-nickel alloy material, ensuring a long life. Their load capacity depends on the operating voltage:
Response Time: Typical switching response time is 25 milliseconds, meeting requirements for fast control.
Mechanical & Electrical Life: Electrical operational life is up to 100,000 cycles; mechanical life is up to 5,000,000 cycles.
Wiring: The 12 relay outputs are connected via the upper 48-point pluggable terminal block (TB1). Each relay occupies 4 terminals (NC, COM, NO, and a reserved SOL terminal).
Integration with the PDIO I/O Module
The IS200TDBSH2A itself has no intelligent processing capability; it must be used in conjunction with a PDIO Discrete I/O Module. The PDIO module plugs into the IS200TDBSH2A via a D-type connector and communicates with the upper-level controller (e.g., Mark VIe controller) over Ethernet. A single TDBS terminal board provides one PDIO connection point, although the PDIO module itself can be configured with one or two network connections to the controller for redundancy.
Pluggable Terminal Blocks
All terminal blocks are pluggable. This is extremely convenient for commissioning, maintenance, or replacement of the terminal board, as the blocks can be unplugged without removing all field wiring, saving significant time and effort.
Working Principles and Detailed Internal Circuitry
(A) Working Principles of the Discrete Input Section
The core task of the discrete input circuit is to reliably convert the mechanical open/close state of field contacts into a digital signal recognizable by the controller.
Wetting Voltage Application and Current Path:
The externally provided 24V DC wetting voltage is supplied to the terminal board via a 3-pin Mate-N-Lok connector (JE1). For the TDBSH2A (as well as H4A, H6A), all 24 wetting voltage output terminals (odd-numbered terminals on TB2) are connected in parallel internally, all sourced from pin 1 of JE1 (positive).
When a field contact closes, a current path is formed: JE1 Pin 1 (+24V) -> Wetting Voltage Terminal (e.g., Wet 1) -> Closed Field Contact -> Input Terminal (e.g., In 1) -> Internal Optoisolator on the Terminal Board -> JE1 Pin 3 (Return Path).
This wiring method—"a single wetting voltage lead to the field, multiple signal lines returning"—is permitted, reducing wiring complexity.
Signal Conditioning and Isolation:
Current Limiting: Resistors in the input loop limit the current to a safe range (2.5mA or 10mA).
Noise Suppression: Filters, consisting of RC networks or transient voltage suppression diodes near the signal entry point, absorb surges and filter out high-frequency noise.
Optical Isolation: This is a key step for system safety. The conditioned voltage signal drives a Light-Emitting Diode (LED). The light from the LED illuminates an internal phototransistor, causing it to conduct, thereby generating a clean signal on the internal side of the board. This physical optical isolation barrier completely separates the field side, which may have high voltages, ground potential differences, and noise, from the control system side, protecting the expensive controller equipment.
Threshold Detection: The input threshold voltage is set at 50% of the wetting voltage (approximately 12V for a 24V nominal voltage). A voltage above this is considered "ON" (1), and below is "OFF" (0).
Difference from IS200TDBSH8A:
It is important to note that the IS200TDBSH8A model has a separate internal current-limiting resistor for each wetting voltage output terminal, requiring a separate wetting voltage lead for each input. The TDBSH2A lacks these resistors; the wetting voltage is distributed directly in parallel.
(B) Relay Output Working Principles and Option Board Expansion
The basic relay output of the IS200TDBSH2A is a "dry contact", meaning the relay coil is driven by the PDIO's internal circuitry, while the relay contacts are entirely user-configured to switch an external load power supply.
Basic Operation:
The PDIO module, based on control logic, sends a drive signal through a connector (JA1) to the coil of a specific relay on the IS200TDBSH2A.
When the relay coil is energized, it pulls in the armature, causing the Common (COM) terminal to switch from connection with the Normally Closed (NC) terminal to connection with the Normally Open (NO) terminal.
The external load's power supply and return path are connected in series between COM and NO (or NC), thus controlling the load via the relay's switching.
Function and Principles of W-Type Option Boards:
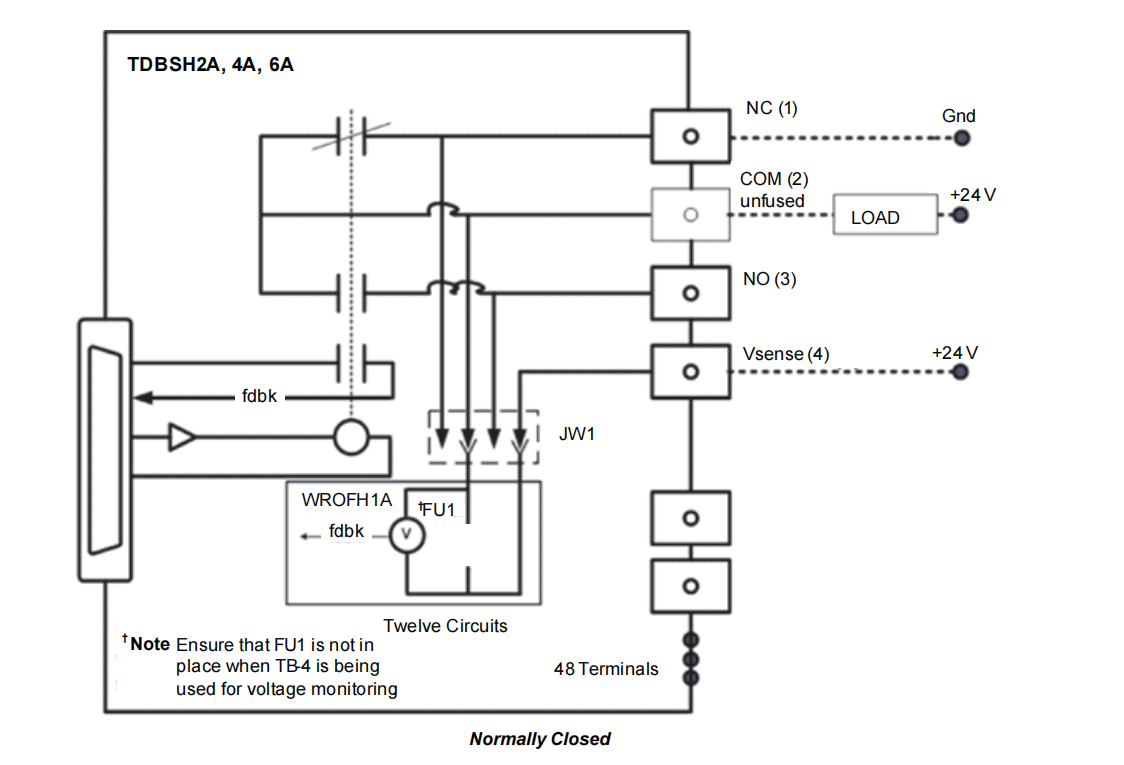
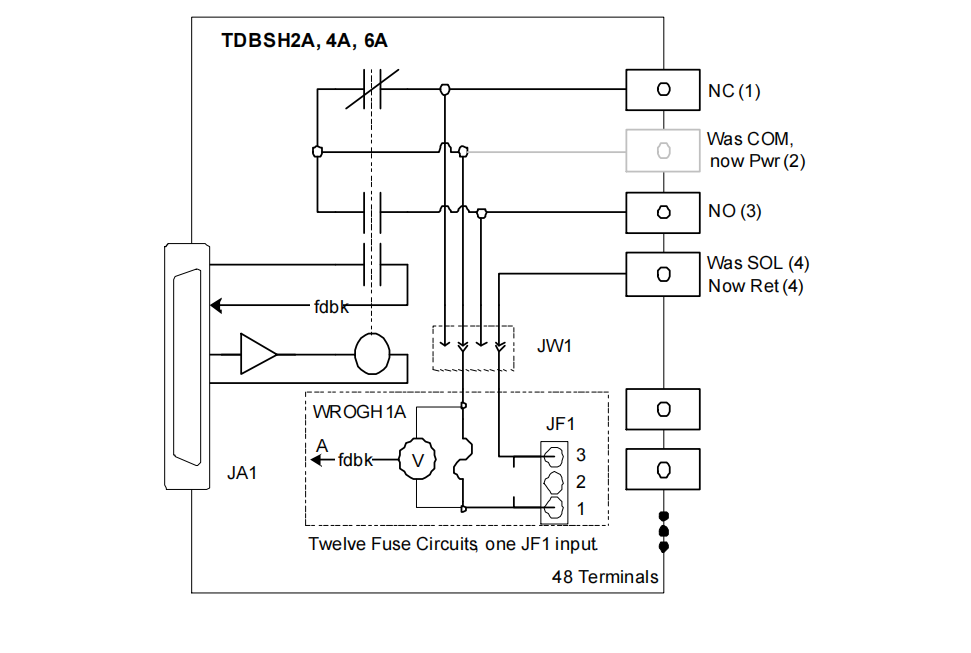
The power of the IS200TDBSH2A (and H4A, H6A) lies in its ability to accept different W-type option boards via connectors JW1 and JW2, expanding simple dry contacts into intelligent outputs with power distribution and diagnostic capabilities.
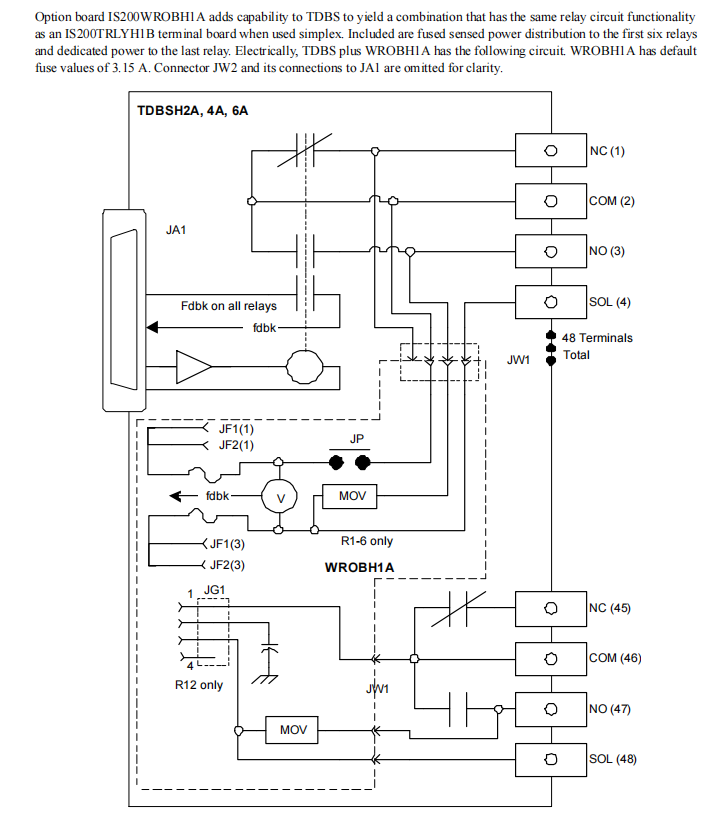
IS200WROBH1A Option Board:
Function: This board provides centralized, fused power distribution for all 12 relays.
Principle: An external power supply is connected via a single input connector (JF1). The positive side of the supply (JF1 Pin 1) is distributed to each relay (the original COM terminal becomes the POWER terminal) after passing through a fuse. The return path for the supply (JF1 Pin 3) is not fused. Similarly, each fuse has isolated voltage feedback for fault diagnosis. This configuration simplifies wiring for applications requiring the same power supply for multiple relays.
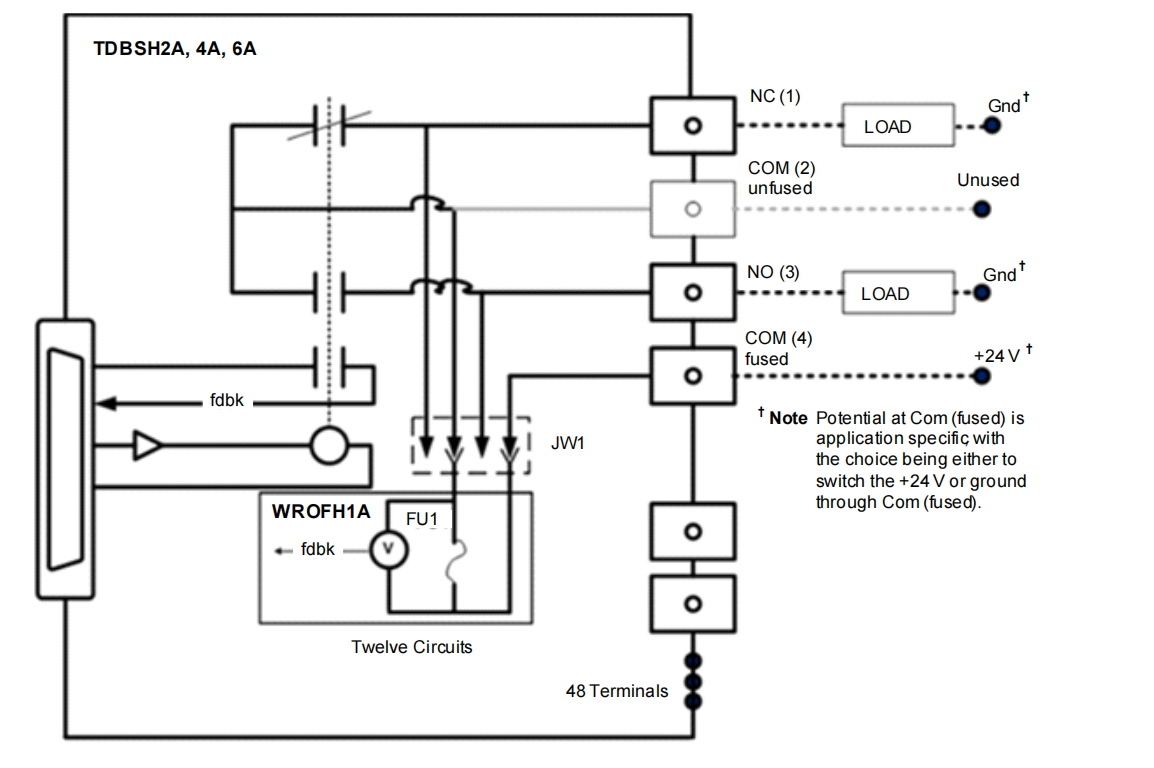
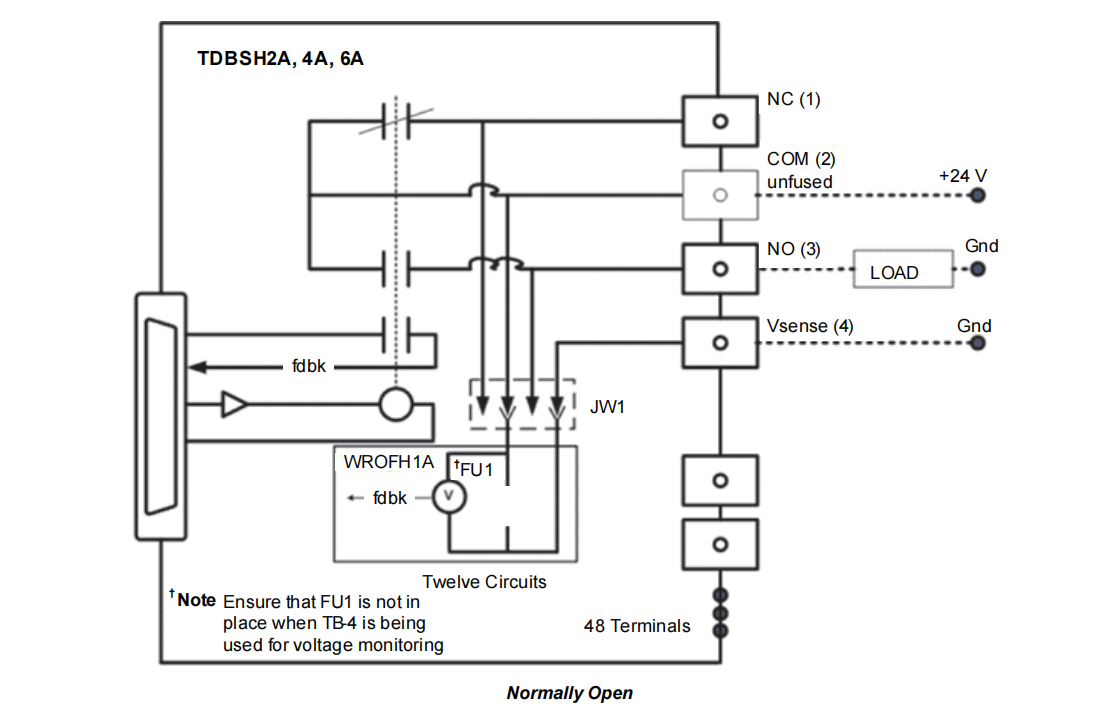
IS200WROFH1A Option Board:
Function: This board places a single fuse in series with the common connection of each relay.
Principle: In use, the load power supply is no longer connected to the basic COM terminal but to the "fused common" terminal provided by the option board. Thus, each output loop is protected by an independent fuse. Simultaneously, the board provides isolated voltage feedback sensing for each fuse, which operates regardless of polarity. The PDIO can monitor this feedback signal. If it detects voltage (meaning power is present on the load side) but the fuse is blown (the circuit is open), it generates a diagnostic alarm. A unique feature is that the user can remove the fuse and wire the fourth terminal (now acting as VSENSE) across the load, effectively turning that circuit into an independent voltage monitor to detect the presence of voltage on the load side, even if the relay is not involved in control.
IS200WROGH1A Option Board:
Function: This board makes the relay portion of the TDBS functionally equivalent to an IS200TRLYH1B terminal board when used in simplex. It provides fused and voltage-sensed power distribution for the first 6 relays (1-6), and dedicated power for the 12th relay.
Principle: A key feature of this board is fusing on both sides. An external power supply (AC or DC) is connected to connectors JF1 and JF2 on the board. Both the positive and negative sides of the supply are fused in series for each output (e.g., FU7 and FU1 correspond to relay 1). This makes it particularly suitable for "floating" systems where the power supply is not grounded. Voltage sensors on the board monitor the voltage across each fuse. If a fuse blows, the sensor detects the voltage difference and feeds a fault signal back to the PDIO. Additionally, Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs) are installed on the Normally Open (NO) contacts to suppress voltage spikes generated by inductive loads.
Installation and Safety Considerations
Mounting: The IS200TDBSH2A is first assembled with a plastic insulator. It can then be snapped onto a standard DIN rail or bolted inside a cabinet using a sheet metal assembly.
Wiring: Use #24 - #12 AWG wires connected directly to the two sets of 48-point pluggable terminal blocks. Shield termination points should be on a separate grounding bar.
Important Warnings:
Hazardous Location Certification: The IS200TDBSH2A is not designed for hazardous locations. If required for hazardous locations, the IS200TDBSH8A model must be selected.
Option Board Usage Restriction: The discrete output option boards (WROBH1A, WROFH1A, WROGH1A) are not certified for hazardous locations and therefore must not be used with the TDBS terminal board in hazardous areas.
Software Version: Do not replace a TDBSH2A with a TDBSH8A without first installing the ControlST software suite version 4.05 or later.
Diagnostics and Configuration