The SB510 is a critical power management module within ABB's Advant Controller 450 industrial automation control system, formally designated as the "Backup Power Supply 110-230 V a.c/d.c." This module is specifically engineered to provide a backup power solution, ensuring the controller's core component—the Random Access Memory (RAM) of the Processor Module—receives continuous and stable power during interruptions or failures of the external main power supply.
As a vital part of the Advant OCS (Open Control System) power architecture, the SB510 works in conjunction with the Battery Unit SB522 to form the last line of defense for controller data retention and system continuity. In application scenarios demanding extremely high system reliability—such as industrial process control, power monitoring, and manufacturing automation—the SB510 is indispensable. It prevents the loss of process data, interruption of control programs, and potential safety risks or production losses caused by unexpected power outages.
The SB510 module features a compact, modular design for installation within a controller subrack, interacting with the system via the backplane bus. Its design complies with industrial environmental standards and incorporates comprehensive diagnostic and protection functions, making it a reliable choice for building highly available and high-integrity control systems.
II. Detailed Main Functions
The functions of the SB510 module are concentrated on ensuring power supply for the Processor Module's RAM, which can be broken down into the following core functionalities:
1. Seamless Mains-to-Battery Switching and Power Supply
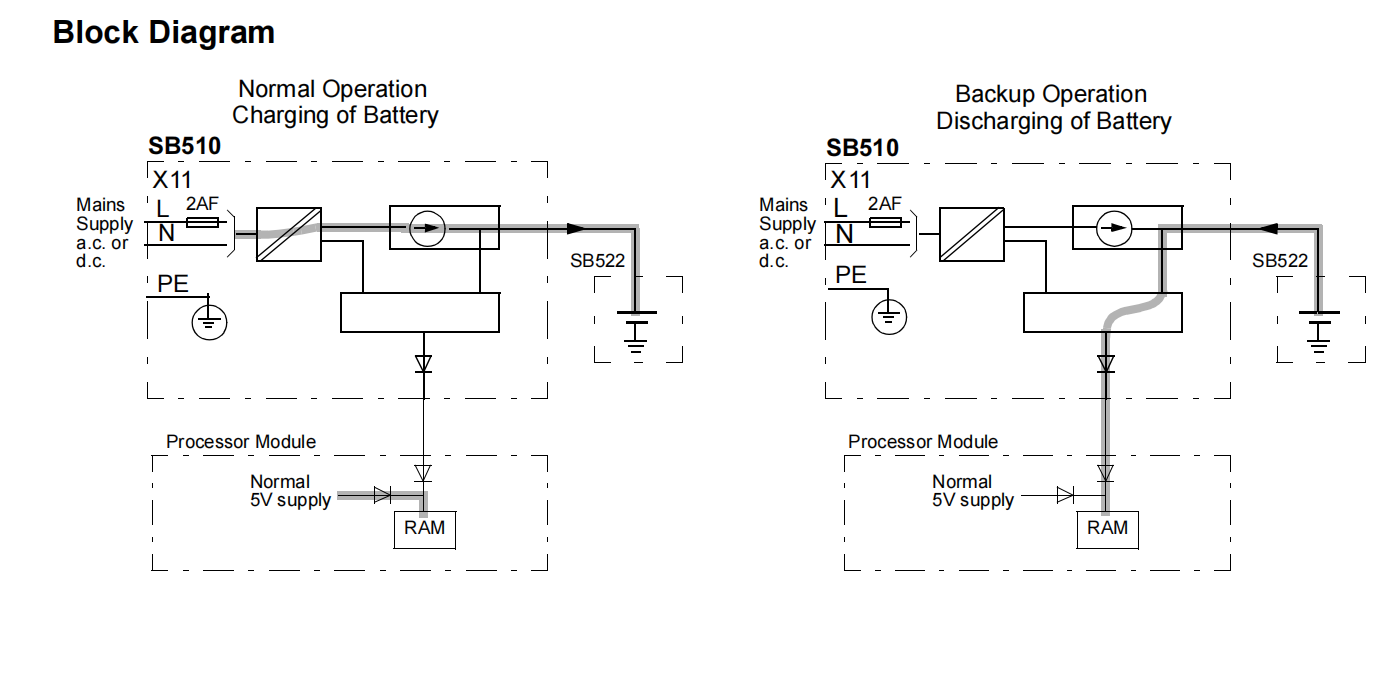
The core function of SB510 is to act as an auxiliary power unit when the external AC or DC mains supply is normal, and to automatically and seamlessly switch to internal battery power when the mains supply fails, is interrupted, or falls outside allowable tolerances. This switching process is performed automatically by the module's internal circuitry without external intervention, guaranteeing that the controller system configuration, runtime parameters, real-time data, and application programs stored in the RAM are not lost due to a power interruption. The data held in RAM is crucial for the control system's normal operation, including process control logic, PID parameters, equipment status, alarm logs, and production data. The backup power function of SB510 provides several hours (standard is a minimum of 4 hours; 2 hours when using redundant processor modules; extendable via parallel configuration) of preservation time for this critical data, buying valuable time for mains power recovery or for executing a safe system shutdown.
2. Intelligent Battery Management and Charging Control
The SB510 is more than a simple backup power source; it is an intelligent Battery Management System (BMS). It is designed for the nickel-cadmium (NiCd) Battery Unit SB522 (nominal 12V, 4Ah) and provides two optimized charging modes:
Recharge Mode: When the module is first powered on, or when it detects that the battery needs replenishment after deep discharge, the SB510 enters a high-current "Recharge" state. In this mode, the charging current is precisely controlled to fully charge a completely depleted 4Ah battery to its rated capacity in approximately 10 hours. A yellow LED labeled "FC" on the module's front panel illuminates to provide a clear visual indication that the system is in the recharge process.
Float/Trickle Charge Mode: Once the battery reaches full charge, the SB510 automatically switches to a low-current float charge mode. This mode compensates for the battery's minimal self-discharge, maintaining it at a near-100% state of charge for immediate readiness, while simultaneously preventing damage from overcharging, thereby maximizing battery lifespan. This intelligent charging management strategy ensures the battery is always on standby while optimizing its service life.
3. Comprehensive Operational Status Diagnostics and Indication
The SB510 incorporates complete diagnostic circuitry that continuously monitors the operational status of the module itself, the input power, and the battery. Diagnostic results are displayed intuitively via five high-brightness LED indicators on the front panel. Furthermore, relevant status information is communicated via the backplane bus to higher-level system status monitoring functions (e.g., the TC520 supervision module) for centralized alarming and logging. The meanings of the indicators are:
F (Fault - Red): Illuminates when the module detects an anomaly, such as excessively low charging current or a low 5V internal auxiliary supply voltage during converter operation (as indicated by the IP LED).
IP (Input Power - Green): Illuminates when the external mains supply (110-230V AC/DC) is properly connected and the module's internal power converter is operational. This is the fundamental indicator of normal module operation.
BP (Battery Powered - Yellow): Illuminates when the external mains supply has failed or is interrupted, indicating the module is currently supplying backup power to the RAM by discharging the internal SB522 battery. This is the key indicator that the system is operating in backup mode.
BF (Battery Fault - Red): Illuminates when a battery-related fault is detected. Possible causes include: deeply discharged battery, battery not connected, internal short circuit or open circuit in the battery, or battery temperature being too low at system startup (affecting performance). This alarm prompts maintenance personnel to check the battery condition.
FC (Fast Charging - Yellow): As mentioned, illuminates to indicate the module is in the battery recharge phase, typically lasting about 10 hours after system power-up or battery replacement.
This multi-layered diagnostic and indication system greatly facilitates status monitoring and rapid fault localization by field engineers and maintenance personnel.
4. Redundant Configuration and Expandability
To meet the demands of applications requiring the highest system reliability, the SB510 supports parallel redundant configuration. By connecting two SB510 modules (with their SB522 batteries) in parallel, a redundant RAM backup power system can be constructed. This configuration not only doubles the backup power duration for the RAM (e.g., from the standard 4 hours to 8 hours) but, more importantly, provides redundancy in the power path. If one SB510 module or its associated battery fails, the other module can take over, ensuring uninterrupted power to the RAM and significantly enhancing the availability of the entire controller's power subsystem. The module's physical output includes a series diode specifically to support this parallel operation mode and prevent current backflow.
5. Electrical Safety and Protection Features
The design of the SB510 fully considers electrical safety requirements for industrial environments:
Input Protection: The module's power input (connector X11) incorporates a front-accessible, replaceable 2AF (Fast-acting) miniature fuse, providing effective protection against risks from input line overcurrent or internal module faults.
Output Protection: The 5V output features short-circuit protection, enhancing system robustness.
Insulation and Grounding: The module complies with IEC 536 Class I protection (earth-protected). Insulation is provided via components like transformers, with a dielectric withstand test of 3.2 kV DC for 2 seconds, ensuring safe isolation between high and low voltage circuits.
Wide Input Range: Supports a broad input range of 110-230V AC or DC (AC allows -15% to +10% variation, DC allows -20% to +20%, with DC input being polarity-insensitive), adapting to grid standards worldwide.
III. In-Depth Working Principle Analysis
The working principle of SB510 can be viewed as a controlled "energy hub" and "power bank." Its internal circuit structure primarily consists of the following functional sections:
1. Power Input and Rectification/Filtering Unit
The externally supplied 110-230V AC or DC power first passes through input connector X11 and fuse 2AF. For AC input, subsequent circuitry includes a rectifier bridge to convert it to pulsating DC voltage; for DC input, it may proceed directly to the filtering stage. This section ensures the module can adapt to both AC and DC inputs and provides preliminary filtering of grid noise.
2. High-Frequency Switching Power Supply Converter
The preliminarily rectified DC power is fed into a high-frequency Switched-Mode Power Supply (SMPS) converter. This is the core energy conversion unit of the module. When the green IP LED is lit, indicating normal converter operation, it performs two main tasks:
* Generates 5V System Auxiliary Power: A portion of the energy is converted into a stable 5V voltage to power the SB510 module's own control circuits, diagnostic circuits, and status indicators.
* Generates Controlled Charging Current: Another portion of the energy is directed to a precise "Controlled Current Generator." Under the control of the module's microprocessor and based on the battery's real-time state (voltage, temperature, etc.) and preset charging algorithms, this generator outputs a precise charging current. In "Recharge Mode," it outputs a higher constant current or a current following a specific curve; in "Float Charge Mode," it outputs a minimal trickle current.
3. Battery Management and Charging Control Logic
This section is the "brain" of the module. It is typically implemented by a microcontroller or dedicated charge management chip, responsible for:
* Mode Determination: Determines whether to enter "Mains Normal - Battery Charging," "Mains Failure - Battery Discharging," or "Fault" state based on input power status, battery voltage, and historical data.
* Charging Algorithm Execution: Controls the "Controlled Current Generator" to implement safe and efficient charging strategies for the NiCd battery, including temperature compensation, trickle transition, etc., to prevent overcharging.
* Battery Status Monitoring: Continuously monitors battery voltage and charging current, and may estimate the State of Charge (SOC) to trigger fault alarms (e.g., BF LED).
4. Output Switching and Voltage Regulation Circuit
This is the key to achieving "seamless switching" functionality. This circuit contains an electronic switch controlled by the input power status and related voltage regulation components.
When Mains Power is Normal: The energy generated by the switching power converter is the primary source. The output circuit is regulated to approximately 5.6V ±0.2V (no load) and directly supplies the processor module's RAM. Simultaneously, surplus energy charges the battery via the charging circuit.
When Mains Power is Interrupted: Input-side energy disappears, and the IP LED extinguishes. The control logic immediately detects this change and switches the electronic switch, causing the circuit to be powered by the SB522 battery (12V). At this point, a boost or voltage regulation circuit activates, converting the battery voltage to a level suitable for the RAM. It is noteworthy that in backup mode, the output voltage is slightly elevated to about 6.0V ±0.2V. The documentation notes this is to compensate for voltage drops introduced by "voting circuitry" in redundant configurations, ensuring the final voltage reaching the RAM remains within specification. The yellow BP LED illuminates to indicate this state.
5. Diagnostics and Communication Interface
Data from all sensors (input voltage, output voltage, charging current, battery voltage, module temperature, etc.) is fed to the management logic for analysis. Any anomaly exceeding thresholds triggers the corresponding fault indicator (F, BF). Simultaneously, the module reports key status information (e.g., "Battery Powering," "Battery Fault") as digital signals via its interface on the subrack backplane to the system's central monitoring unit. This facilitates integration into the plant's Equipment Health Management (EHM) or the Distributed Control System's (DCS) alarm lists.
IV. Installation, Maintenance, and Operational Guidelines
1. Installation Steps
Module Insertion: First, correctly insert the SB510 module into the designated slot in the controller subrack.
Power Connection: CRITICAL: After the module is inserted, connect the external mains power cable to the front connector X11. Always follow safe operating procedures: "earth first, then line/neutral," and ensure reliable grounding.
Battery Connection: Reliably connect the SB522 Battery Unit to the SB510 module's battery interface using the specified cable.
Status Confirmation: After powering up, observe the indicators: Green IP LED should be steady on, yellow FC LED may be on (indicating charging), and other fault LEDs should be off. If abnormal, power down and investigate.
2. Routine and Preventive Maintenance
Regular Inspection: Periodically (e.g., quarterly or semi-annually) visually inspect all LED indicator statuses to confirm no red fault LEDs are illuminated.
Battery Maintenance: NiCd batteries have a finite lifespan and can suffer from memory effect. Even if the system experiences no power loss, it is advisable to perform a complete "discharge-recharge" cycle per manufacturer guidelines or every 2-3 years to calibrate battery capacity and maintain its activity. Monitoring the frequency of BF and BP LED anomalies can serve as a reference for battery aging.
Fuse Replacement: If the module is completely unresponsive and input power is confirmed normal, after disconnecting all power, inspect and replace the front-accessible 2AF fuse.
Cleaning: With power disconnected, use a dry cloth or anti-static brush to clean dust from module ventilation slots and surfaces.
3. Fault Diagnosis Guidance
F (Fault) Red LED On: Check if the system 5V bus is normal, or contact qualified personnel for internal module inspection.
BF (Battery Fault) Red LED On: Check if battery connectors are loose; measure battery voltage to determine if over-discharged (requires extended charging) or damaged (requires replacement); check if ambient temperature is too low.
BP (Battery Powered) Yellow LED Steady On: Verify if external mains power is indeed interrupted. If mains power is normal but BP LED is on, it may indicate a fault in the SB510's input detection circuit or the main power input line.
All LEDs Off: Check input power, fuse, and whether the module is properly seated.
VI. Application Scenarios and System Integration Advantages
The SB510 is typically applied in the following scenarios with stringent requirements for power continuity:
Continuous Process Industries: Chemical, petroleum refining, pharmaceutical industries, where unexpected controller shutdowns can lead to batch loss, equipment damage, or even safety incidents.
Power System Monitoring and Protection: In power plants and substations, controller data forms the basis for grid operation status and fault analysis and must not be lost.
Critical Infrastructure: Water treatment, data center environmental control, etc.
High-End Manufacturing: Automotive manufacturing, semiconductor production lines, where the high value of production programs and data demands extremely high system availability.
The advantages of integrating SB510 within the Advant Controller 450 system include:
Seamless Integration: Perfect match in hardware dimensions, backplane interface, and diagnostic signals with the controller architecture.
Centralized Management: Its status can be collected by system monitoring modules like TC520 for centralized alarm display on operator stations, enabling predictive maintenance.
Improved Overall MTBF: By providing reliable RAM backup power, it effectively prevents full system restarts and data loss caused by short-term power disturbances, significantly increasing the controller's Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF).
Flexible Power Solutions: Supports AC/DC input, single/ redundant configuration, allowing flexible setup based on site power conditions and reliability requirements.
VII. Safety Precautions
Professional Installation: Installation, wiring, and maintenance must be performed by trained professionals familiar with relevant electrical safety regulations.
De-energized Operation: Before performing any wiring, module insertion/removal, or fuse replacement, ensure the relevant circuits are completely de-energized and verified dead.
Battery Safety: NiCd batteries contain corrosive electrolyte. Avoid short-circuiting, disassembling, incinerating, or exposing batteries to extreme temperatures. Use specified models for replacement.
Grounding is Critical: Ensure the protective earth (PE) connection for the SB510 module and its cabinet is secure and reliable. This is fundamental for personnel safety and equipment noise immunity.
ESD Precautions: Employ appropriate anti-static measures, such as wearing a grounded wrist strap, when handling circuit boards.
Comply with Local Regulations: Installation and operation must comply with all applicable national and local electrical safety codes and standards.