The IS200TPROH1C Emergency Protection Terminal Board is a critical component within the Mark VI Turbine Control System, specifically designed to implement an independent emergency overspeed (EOS) and synchronization check protection system, separate from the primary control system. It acts as a highly reliable signal interface unit, responsible for collecting critical protection signals from the turbine and distributing them to triple-redundant VPRO protection boards for processing. The core design philosophy of the TPRO is to provide a reliable "last line of defense," ensuring that a turbine trip can be effectively triggered to protect the equipment even if the main control system fails.
This terminal board does not rely on Mark VIe I/O packs and is an independent hardware entity. Its design adheres to the principles of high-integrity protection systems, utilizing redundancy, isolation, and diagnostic technologies to minimize the probability of both false trips and failure to trip.
2. System Architecture and Functional Role
The IS200TPROH1C plays the role of a signal aggregation and distribution hub within the protection system architecture. The entire emergency protection system primarily consists of three parts:
IS200TPROH1C Terminal Board: Responsible for receiving all raw protection signals from field sensors.
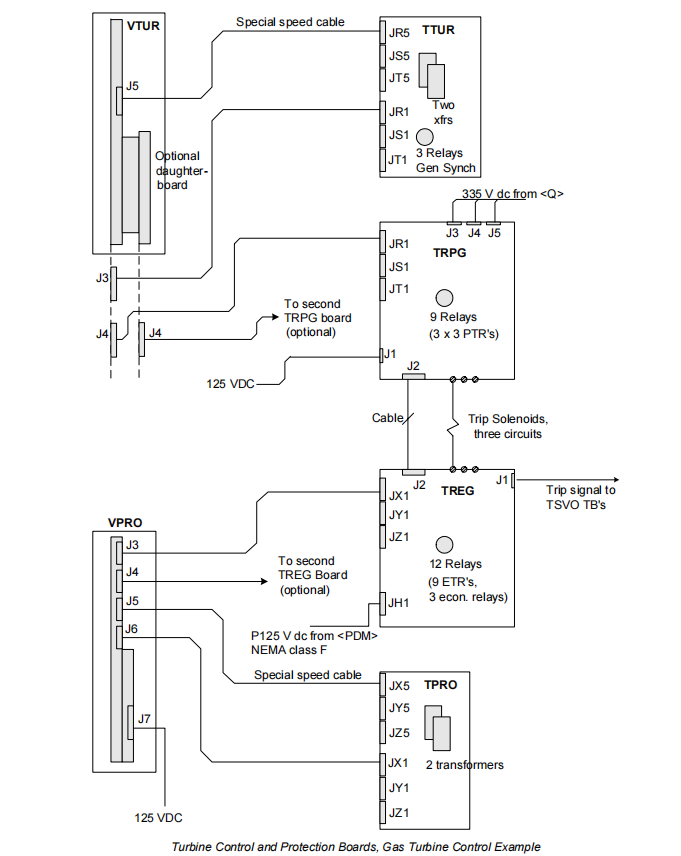
Triple-Redundant VPRO Protection Boards (VPRO-R8, VPRO-S8, VPRO-T8): Receive signals from the IS200TPROH1C, independently execute protection logic (e.g., overspeed determination, synchronization check), and output trip commands.
TREx Trip Relay Boards (e.g., TREG): Receive commands from the VPRO and directly control the power circuit of the trip solenoids.
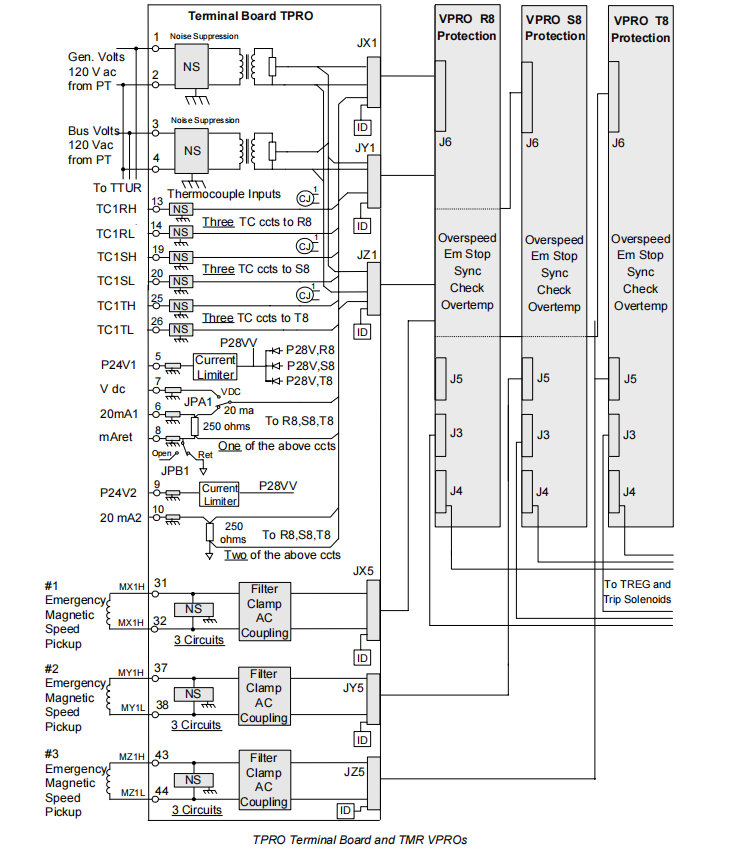
The core function of the IS200TPROH1C is to provide identical, isolated input signals to all three VPRO boards simultaneously. This means that every signal, from speed pickups to voltage transformers and thermocouples, is paralleled and distributed by the TPRO to three independent VPRO channels. This architecture is the foundation for achieving a Triple Modular Redundant protection system, ensuring that a single VPRO board or signal path failure does not lead to the loss of the entire protection function.
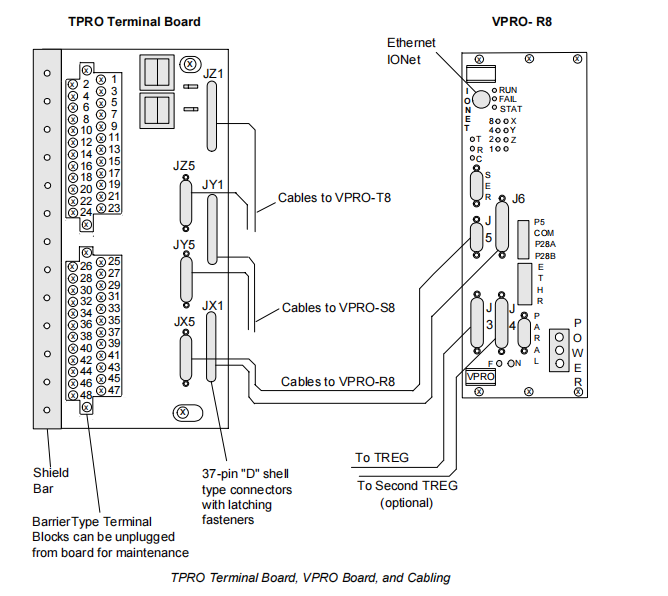
The system workflow is as follows: Sensor signals are wired to the TPRO -> TPRO distributes signals in parallel to the three VPROs -> Each VPRO independently executes its logic -> The VPROs vote, via relays on the TREx board, to decide whether to energize the trip solenoids. The TPRO connects to the VPRO boards via 37-pin "D"-shell connectors with latching fasteners, ensuring connection reliability. Furthermore, the terminal blocks on the TPRO are of a barrier-type design and can be unplugged entirely from the board, significantly facilitating maintenance and wiring work.
3. Detailed Functions and Operating Principles
3.1 Emergency Overspeed Protection Function
This is the most critical function of the IS200TPROH1C. Its principle is to monitor the turbine speed and trigger an emergency shutdown when the speed exceeds a safe setpoint.
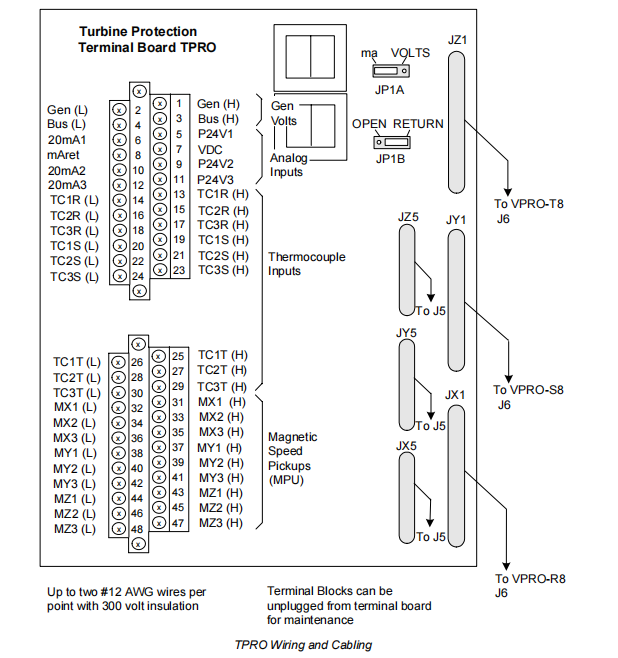
Signal Acquisition: The IS200TPROH1C terminal board is designed to connect up to nine passive magnetic speed pickups. These nine pickups are typically divided into two groups: one group (the first three) supplies the main controller for speed control and primary overspeed protection; the other group (the next three or more) is dedicated to the IS200TPROH1C for emergency overspeed protection. The TPRO routes the signals from these emergency overspeed pickups to the three VPRO boards via separate cables and connectors, with each VPRO receiving a signal from one pickup.
Signal Processing and Transmission:
The magnetic pickups sense gear teeth, generating a sinusoidal voltage signal. The signal amplitude and frequency increase with rising speed.
The input circuitry on the IS200TPROH1C board processes these high-frequency signals. Its input circuit has specific load characteristics and boasts a wide pulse rate range and high sensitivity.
The pickups can be located up to 300 meters from the IS200TPROH1C cabinet using shielded twisted-pair cable, offering strong noise immunity.
Redundancy Logic: The three VPRO boards independently calculate the speed based on their respective received signals. The emergency trip command typically uses a "two-out-of-three" voting logic; that is, the system will only initiate a trip if at least two VPROs simultaneously detect an overspeed condition. This prevents both false trips due to a single pickup or VPRO failure and failure to trip due to a single channel fault.
3.2 Backup Synchronization Check Protection Function
This function prevents the generator breaker from closing when the generator and grid are not synchronized, thereby avoiding massive mechanical and electrical stress damage to the generator and the grid.
Signal Acquisition: The IS200TPROH1C receives signals from the secondary side of two single-phase potential transformers: Generator Voltage and Bus Voltage. These signals are typically rated at 115 V RMS.
Signal Distribution and Isolation: The TPRO internally parallels these two voltage signals and distributes them to the three VPRO boards. Each PT input is magnetically isolated within the TPRO, featuring a 1500 V RMS rated isolation barrier, and each PT input presents a load of less than 3 VA, ensuring signal accuracy and safety.
Operating Principle: Each VPRO board contains a high-precision sync-check module that continuously monitors the voltage magnitude difference, frequency difference, and phase angle difference between the generator and bus voltages.
Protection Output: A permit signal is only issued when the "synchronized" conditions from the three VPRO channels are confirmed through the voting logic. This drives the K25A relay on the TREG board. The contacts of the K25A relay are wired in series with the main sync-permit relay and auto-sync relay contacts. This hardwired series connection forms a robust safety interlock: the generator breaker close command can only be issued if the backup sync-check, the main sync system, and other permits are all granted, effectively preventing false closing commands.
3.3 Thermocouple and Analog Input Functions
The IS200TPROH1C also provides additional analog protection input channels for the gas turbine, primarily used for backup temperature and process parameter protection.
Thermocouple Inputs: The IS200TPROH1C provides 9 thermocouple inputs, primarily used for backup exhaust over-temperature protection on gas turbines. These 9 thermocouples are evenly distributed to the three VPRO boards, with each VPRO receiving 3. This distribution provides redundancy: even if the temperature measurement function of one VPRO channel fails completely, the other two channels can still perform the over-temperature protection.
Analog Inputs: The IS200TPROH1C provides 3 analog inputs:
1 multi-function input: Configurable via jumpers JP1A and JP1B to accept a 4-20 mA current signal, ±5 V DC, or ±10 V DC voltage signal.
2 dedicated 4-20 mA current inputs.
These analog inputs can be used to monitor critical parameters such as lube oil pressure or fuel gas pressure, serving as backup protection to the main control system. The VPRO boards supply 28 V DC power for these sensors. This power is conditioned through circuits on the TPRO before the standard 4-20 mA signals are sent to the three VPROs.
4. Hardware Design and Installation
The IS200TPROH1C is a standalone terminal board measuring 17.8 cm Wide x 33.02 cm High, designed for direct mounting to the panel sheet metal, typically using a keyhole mounting scheme.
Terminal Blocks: The terminal blocks on the board are clearly divided into functional areas, including Generator/Bus Voltage, Analog Inputs, Thermocouple Inputs, and Magnetic Speed Pickup Inputs. Each terminal can accept up to two #12 AWG wires with 300-volt insulation.
Maintainability: The barrier-type terminal blocks can be unplugged as a whole from the circuit board, which is extremely convenient for wire replacement or inspection without handling the board itself.
Connectors: Connection to the three VPRO boards is achieved via 37-pin "D"-shell connectors, which feature latching mechanisms for reliable connection in vibrating environments.
Power: The VPRO boards supply 28 V DC power to the TPRO, specifically used to power the connected analog sensors.
5. Diagnostics and Maintenance
The IS200TPROH1C and VPRO system incorporate comprehensive online diagnostics to ensure the health of the protection system.
Signal Diagnostics: The VPROs continuously monitor all input signals from the TPRO. If an analog input exceeds preset high/low limits, or if the signal quality is abnormal, the VPRO will generate a fault.
Hardware Identification and Compatibility Diagnostics: The connectors on the TPRO terminal board incorporate a read-only identification chip. This chip is coded with the terminal board's serial number, board type, revision number, and plug location. When the VPRO board powers up or operates, it reads this ID information. If a mismatch is detected, the VPRO immediately generates a "hardware incompatibility" fault, preventing protection function anomalies caused by incorrect hardware configuration.
Alarm Summary: If any signal from the TPRO or its connecting cables is diagnosed as unhealthy, a corresponding composite VPRO diagnostic alarm is triggered. These diagnostic signals can be individually latched and reset once the signal returns to a healthy state.