The IS200STCIH4A is a specialized member of the STCI (Simplex Contact Input) terminal board family, engineered for GE's Mark VIe and Mark VIeS Control Systems. While sharing the compact form factor of its STCI siblings, the IS200STCIH4A is distinctly characterized by its 48 V DC wetting voltage specification. This design positions it as the optimal solution for industrial applications involving longer cable runs, electrically noisier environments, or interfaces with legacy equipment and sensing devices that operate on standard 48 V DC control circuits.
The terminal board serves as the critical interface point, connecting 24 field dry contacts to a single PDIA or YDIA I/O pack in a Simplex configuration. Its architecture is built upon group isolation principles and incorporates robust signal conditioning to ensure data integrity. The IS200STCIH4A is equipped with pluggable Euro-style terminal blocks, a feature that significantly accelerates installation and simplifies maintenance procedures by allowing wiring to be performed off-line.
2. Hardware Architecture & Electrical Interface
The physical and electrical design of the IS200STCIH4A is tailored for reliability and serviceability in demanding conditions.
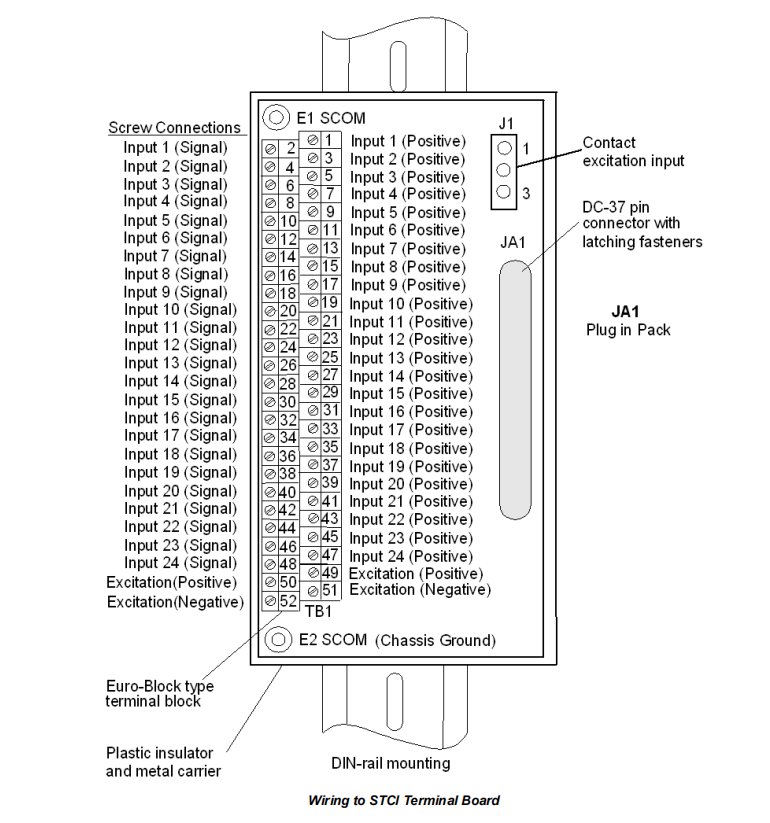
Mechanical Profile: The board features a compact footprint measuring 15.9 cm in height and 10.2 cm in width. It is mounted via a plastic insulator onto a metal carrier, which is secured to a standard DIN rail. An alternative flat-mounting option using a sheet metal assembly is also available.
Pluggable Terminal System: A primary feature is the use of pluggable Euro-style terminal blocks, secured by two screws. This allows the entire terminal block assembly to be disconnected from the main PCB for effortless wiring or replacement without disturbing the field wiring or the connected I/O pack.
Connector System:
JA1 (DC-37): This is the primary system interface, providing a direct, latching connection for the PDIA or YDIA I/O pack. It carries the 24 conditioned input signals, power, and communication lines for ID and feedback multiplexing.
Power Input Terminals: The 48 V DC floating wetting voltage is supplied through dedicated terminals (e.g., terminals 50 for positive and 51/52 for negative) on the terminal block. The allowable input range is 32 to 60 V DC.
Grounding: Dedicated SCOM screw terminals (E1, E2) provide a secure connection to chassis ground, which is essential for proper shield termination and noise immunity.
3. Functional Operation & Signal Integrity Assurance
The IS200STCIH4A's operation is a multi-stage process focused on translating a physical contact closure into a pristine, digitally-readable signal for the controller.
3.1 Excitation and Initial Signal Conditioning
The functional chain begins with the application of the 48 V DC wetting voltage. This floating power source is routed through the terminal board and made available at each of the 24 input pairs. A field dry contact (e.g., from a relay, limit switch, or pushbutton) is wired across the positive and return terminals for a specific channel. The closure of this contact completes the circuit, allowing current to flow.
Immediately upon entry, each input is subjected to rigorous conditioning:
Noise and Surge Suppression: Each channel is protected by a dedicated network designed to clamp high-voltage transients and filter out high-frequency electromagnetic interference (EMI). This is particularly critical for 48V systems often used in environments with motor drives and power equipment, ensuring that electrical noise does not cause false triggering.
Hardware Filtering: A fixed 4-millisecond hardware filter is integrated into each channel. This filter effectively eliminates signal chatter caused by mechanical contact bounce, providing a debounced, stable signal to the I/O pack. This hardware-based debouncing is more robust and deterministic than software solutions.
3.2 Signal Transmission and I/O Pack Processing
The conditioned 48 V DC signals are passed in parallel to the I/O pack via the DC-37 connector. The subsequent processing, while performed by the I/O pack, is a direct continuation of the terminal board's function:
Opto-IsoIation and Level Shifting: Within the I/O pack, each signal is passed through an opto-coupler. This device uses light to transfer the signal, creating a 1500 V isolation barrier between the field-side circuitry (on the STCIH4A) and the sensitive control-side electronics. This prevents ground loops, mitigates common-mode noise, and protects the control system from damaging voltage surges originating in the field.
Variable Threshold Detection: The input circuit employs a comparator with a variable threshold derived from the wetting voltage. For the IS200STCIH4A, this threshold is typically set at 50% of the applied 48 V DC (approximately 24V). This intelligent design ensures consistent "ON"/"OFF" detection across the specified voltage range (32-60 V DC). The system incorporates a fail-safe mechanism: the threshold is clamped to a minimum of 13% of the nominal voltage, forcing all inputs to a safe "OFF" state if the wetting voltage is lost.
Undervoltage Monitoring: The I/O pack continuously monitors the wetting voltage. If it drops below 40% of the nominal 48 V DC, a diagnostic alarm is generated and latched, alerting operators to a potential power supply issue.
4. Electrical Characteristics & Diagnostic Capabilities
4.1 Input Current Profile
The IS200STCIH4A's input circuits are designed with specific impedance to limit current flow, protecting both the field contact and the internal electronics. The current draw is not uniform across all channels:
Channels 1-21: Each channel draws approximately 2.5 mA when the contact is closed.
Channels 22-24: These three channels are designed with a lower impedance, drawing approximately 10 mA each. This provides greater sink capability, making them suitable for interfacing with devices like solid-state outputs or certain proximity sensors that require a stronger pull-down current.
4.2 Integrated Diagnostic Framework
The collaboration between the IS200STCIH4A and its I/O pack enables a comprehensive diagnostic strategy:
Electronic ID Verification: The terminal board contains an embedded ID chip. Upon connection, the I/O pack reads data including the board's serial number, type (IS200STCIH4A), and revision. This is cross-referenced with the configuration in the ToolboxST software. A mismatch immediately generates a hardware fault, preventing operation with an incorrect or unapproved component.
Periodic Input Self-Test: The I/O pack executes an automated self-test routine every four seconds. It momentarily perturbs the detection threshold for each input and verifies that the opto-coupler responds correctly. An input that fails to respond is flagged with a specific alarm (e.g., "Contact Input [#] not responding"), identifying the precise channel for maintenance.
5. Installation and Configuration
5.1 Installation Workflow
Mount the terminal board on a DIN rail or panel.
Wire the 48 V DC wetting power source and all 24 field contacts to the pluggable terminal block.
Connect the SCOM terminals to chassis ground.
Plug the assembled terminal block into the main PCB.
Attach the PDIA or YDIA I/O pack to the DC-37 connector and secure it with the side mounting studs.
Connect Ethernet and 28V power to the I/O pack.
5.2 Configuration Parameters (in ToolboxST)
Key software parameters for the associated I/O pack include ContactInput (Used/Unused), SignalInvert, SeqOfEvents recording, and an optional software SignalFilter to complement the built-in 4ms hardware filter.
6. Detailed Comparison: IS200STCIH4A vs. IS200STCIH2A
The choice between the IS200STCIH4A and IS200STCIH2A is primarily driven by application-specific electrical requirements rather than functional differences. The following table outlines their key distinctions.
| Feature/Aspect | IS200STCIH4A | IS200STCIH2A | Implication of the Difference |
| Nominal Wetting Voltage | 48 V DC | 24 V DC | The IS200STCIH4A is designed for higher voltage control circuits. This provides greater noise immunity over long cable runs and is often a standard in specific industries or for interfacing with legacy 48V systems. |
| Operating Voltage Range | 32 - 60 V DC | 18.5 - 32 V DC | The IS200STCIH4A accommodates a wider and higher range of input excitation voltages, offering more flexibility and tolerance in systems with fluctuating power supplies. |
| Input Current (Ch 1-21) | ~2.5 mA | ~2.5 mA | The current draw for the first 21 channels is identical, as the internal impedance scales with the wetting voltage to maintain the same current. |
| Input Current (Ch 22-24) | ~10 mA | ~9.9 mA | The higher current in the last three channels of the IS200STCIH4A is due to the higher voltage and proportionally scaled-down resistance, resulting in a similar power dissipation but a stronger sink capability. |
| AC Noise Immunity | 24 V RMS rejection at 48V excitation | 12 V RMS rejection at 24V excitation | The higher wetting voltage inherently provides a superior signal-to-noise ratio. The IS200STCIH4A can reject significantly higher levels of AC interference without false triggering, making it more robust in electrically noisy environments (e.g., near heavy machinery, motor control centers). |
| Typical Application Context | Preferred for long-distance wiring, high-noise industrial plants, and integration with 48V legacy control systems. | Ideal for standard industrial panels with shorter cable runs, modern 24V sensor/actuator networks, and general-purpose applications where 24V is the standard control voltage. | The selection is not interchangeable without also changing the wetting power supply and ensuring compatibility with the field devices' voltage ratings. |
| Internal Circuit Impedance | Higher impedance per channel to limit current at 48V. | Lower impedance per channel to limit current at 24V. | The physical components (resistors) on the terminal board are different to achieve the correct current limiting for their respective voltage classes. |
Summary of Differences: The IS200STCIH4A is not a direct substitute for the IS200STCIH2A but a specialized variant for higher-voltage applications. Its 48 V DC operating voltage is its defining characteristic, which directly translates into enhanced noise immunity and suitability for longer cable runs. Selecting the IS200STCIH4A over the IS200STCIH2A is a deliberate choice for overcoming specific electrical environmental challenges or meeting legacy system voltage requirements.