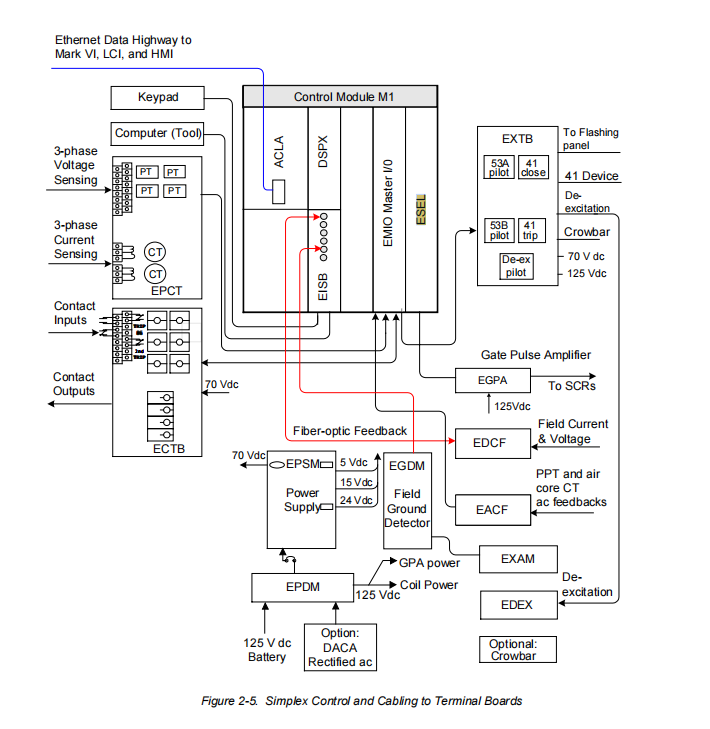
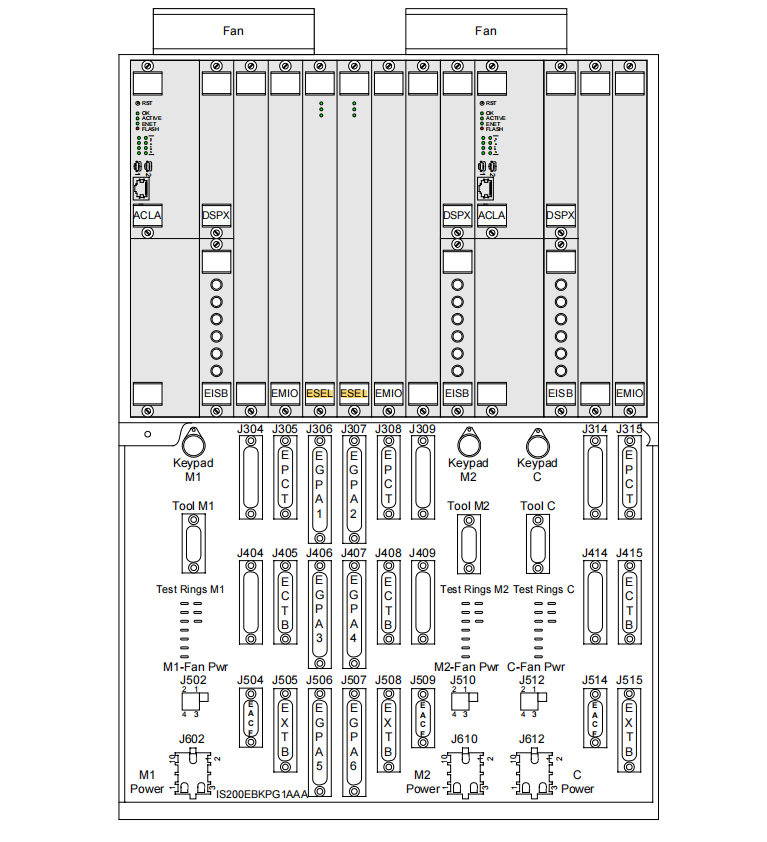
The IS200ESELH1A is a dedicated Exciter Selector Board within GE's EX2100 static excitation control system. This board serves as a critical component in the EX2100 redundant control architecture, responsible for the final selection and routing of thyristor gate trigger pulses within dualized control system configurations.
The "H1" designation in its model number indicates its design purpose: to drive a single Power Conversion Module (PCM). It is installed within the VME-standard control module of the control cabinet and interacts with core controllers such as the Digital Signal Processor board (DSPX) and the Main I/O board (EMIO) via the Exciter Backplane (EBKP). Its primary design objective is to ensure the bumpless transfer of control authority from the active controller to the standby controller in the event of an active controller failure, thereby guaranteeing the continuity and high reliability of generator excitation control.
II. In-Depth Analysis of Core Functions
The functionality of the IS200ESELH1A extends far beyond that of a simple signal pass-through; its design embodies the essence of highly reliable industrial control systems.
1. Reception and Routing of High-Precision Gate Pulses
This is the most fundamental and critical function of the IS200ESELH1A. Within the EX2100 control logic, the DSPX board, at the top of the control chain, executes core regulatory algorithms and ultimately generates logic-level gate pulse signals with precise timing and phase. These pulses control the turn-on and turn-off of the six thyristors (SCRs) in the three-phase full-wave thyristor bridge. These pulse signals are first sent to the EMIO board for I/O management and are then transmitted via the control backplane (EBKP) to the IS200ESELH1 board.
Precise Reception: The IS200ESELH1A reliably receives these six logic pulse signals from its corresponding EMIO board. These six signals correspond precisely to the firing commands for the six SCRs in the power bridge.
Dedicated Routing: As an H1 model, it is specifically tasked with transmitting the received pulse signals, via a set of output cables, completely and accurately to the Exciter Gate Pulse Amplifier board (EGPA) corresponding to one and only one Power Conversion Module. This "one-to-one" drive design clearly defines its application scope within the system, suitable for standard single-bridge configurations or excitation systems with basic redundancy requirements.
2. Core Arbitration and Bumpless Transfer in Redundant Control Architecture
This represents the most significant value of the IS200ESELH1A in a redundant configuration and is key to achieving high availability in the EX2100 system. In systems with redundant controllers (typically a Triple Modular Redundant - TMR architecture comprising M1-Master 1, M2-Master 2, and C-Coordinator/Selector controllers), the IS200ESELH1A is the physical execution unit for the "bumpless transfer" function.
Dual-Channel Configuration: In a redundant system, two IS200ESELH1A boards operate in parallel, one belonging to the M1 control division and the other to the M2 control division. This means that for the same power bridge, the system is always prepared with two completely independent and parallel gate pulse command streams.
Arbitration Logic Execution: The Coordinator controller (C), while not directly involved in pulse generation, plays a crucial role. It continuously monitors the comprehensive status of both master controllers, M1 and M2, including processor heartbeat, computational result consistency, and hardware self-diagnostic status. Through a complex set of voting and diagnostic algorithms, controller C arbitrates in real-time which master controller is the current "Active Master Controller," deemed the healthiest and most reliable.
Physical Channel Gating: Based on the arbitration result from controller C, the system sends "Enable" or "Disable" electronic commands to the two IS200ESELH1A boards. Only the IS200ESELH1A board in the control division designated as active will open its internal signal pathway, allowing the six pulse signals it receives to pass through to the output port connected to the EGPA board. The output channel of the other, standby IS200ESELH1A board is strictly logically blocked, even though it internally continues to receive pulse signals from its master controller.
The Pursuit of Bumpless Transfer: When the active master controller in operation (e.g., M1) is detected to have any unrecoverable fault or performance degradation, controller C makes a decision within milliseconds, revoking the enable signal for the M1 division's IS200ESELH1A board and simultaneously granting the enable signal to the M2 division's IS200ESELH1A board. Because the standby controller M2 continuously tracks the system state via software algorithms, its output firing pulses are highly synchronized in phase with the master controller M1. Consequently, this switching process causes almost no disturbance to the output current of the power bridge. The generator terminal voltage and reactive power remain stable, achieving a true "bumpless transfer" and significantly enhancing the operational reliability and continuity of the generator set.
3. Hardware Safeguard for System Security and Reliability
The design of the IS200ESELH1A incorporates multiple safety concepts.
Fault Isolation: By physically blocking the pulse output of the non-active controller, it effectively prevents faulty controllers from sending erroneous or dangerous firing commands to the power bridge, avoiding potential equipment damage or system oscillations due to control logic corruption.
Clear Division of Labor: The H1 model is dedicated to single-bridge drive, which clarifies the system architecture and simplifies fault troubleshooting. During maintenance or inspection, technicians can precisely locate the control chain for a specific power bridge.
III. Working Principle and System Integration Deep Dive
The operation of the IS200ESELH1A is a dynamic, controlled, and highly reliable signal selection and gating process.
1. Signal Flow Under Normal Operation (Example: M1 as Active Master)
Step 1: Pulse Generation. Within the M1 control division, the DSPX board calculates the deviation between the generator terminal voltage and the setpoint in real-time. Through PID and other regulatory algorithms, it determines the required thyristor firing angle and generates six corresponding logic pulse sequences, strictly synchronized to the AC line voltage zero-crossings.
Step 2: Internal Transmission. These pulses are passed via the backplane bus to the EMIO board within the same M1 division. The EMIO board performs necessary I/O management and logic processing, then routes the pulse signals through the dedicated path on the backplane to the M1-ESEL slot, delivering them to the IS200ESELH1A board.
Step 3: Arbitration & Enable. The Coordinator controller (C) continuously broadcasts its arbitration status to both IS200ESELH1A boards via a high-speed communication bus (e.g., ISBus) on the backplane. At this time, the M1 division's IS200ESELH1 board continuously receives the "Active" command, and its internal electronic switch is in the "closed" state.
Step 4: Signal Output. Consequently, the six pulse signals from the EMIO pass smoothly through the IS200ESELH1A board and are transmitted via its front-panel, high-density D-SUB connectors and shielded cable bundles to the EGPA board located in the power conversion cabinet.
Step 5: Power Drive. The EGPA board acts as the final execution unit, amplifying the weak logic pulses from the control cabinet and providing electrical isolation, converting them into powerful pulses with sufficient energy and voltage level to directly drive the gates of the SCRs, controlling their conduction and thereby generating the required DC excitation current.
2. Dynamic Principle of Redundant Switching Process
Detection & Decision: Controller C detects a critical fault in the M1 controller (e.g., software crash, hardware error). This process is accomplished through hardware watchdogs and software health diagnostics.
Command Switching: Upon confirming the fault, controller C immediately (typically within 10-50 milliseconds) sends new arbitration commands via the backplane to the two IS200ESELH1A boards: "Disable M1-ESEL, Enable M2-ESEL."
Physical Switching: The M1 division's IS200ESELH1A board, upon receiving the disable command, instantly cuts off its internal signal path, and its output becomes a high-impedance state or no-signal state. Almost simultaneously, the internal path of the M2 division's IS200ESELH1A board is connected.
Seamless Handover: Because the DSPX of the M2 controller has been tracking the actual system state, the pulse sequence it generates closely matches the phase of M1's pulses at the moment of switching. Therefore, when M2-ESEL connects, the pulse sequence received by the EGPA board does not undergo a sudden jump in time or phase. The output current of the power bridge transitions smoothly, the generator's excitation field experiences no impact, and the system load is entirely unaware of this internal switchover.