| Core Application Voltage | Nominal 125V DC (Range: 100-145V DC) | Nominal 24V DC (Range: 16-32V DC) | The most fundamental difference. H6A for high-voltage field instruments, H2A for standard low-voltage applications. |
| Input Current | ~2.55mA (first 21), ~10mA (last 3) @125V DC | ~2.5mA (first 21), ~10mA (last 3) @24V DC | Current values are similar, but H6A achieves this with higher-value current-limiting resistors to withstand the high voltage. |
| AC Voltage Rejection | 60V RMS (at 125V DC wetting) | 12V RMS (at 24V DC wetting) | H6A has significantly higher noise immunity, suitable for harsher EMI environments. |
| Input Threshold Voltage | ~62.5V DC (50% of 125V DC) | ~12V DC (50% of 24V DC) | The high threshold is the basis for H6A's high noise immunity. |
| Internal Current Limiting | High-resistance current-limiting resistors in input circuits | Low-resistance current-limiting resistors in input circuits | A key hardware difference to adapt to different voltages. |
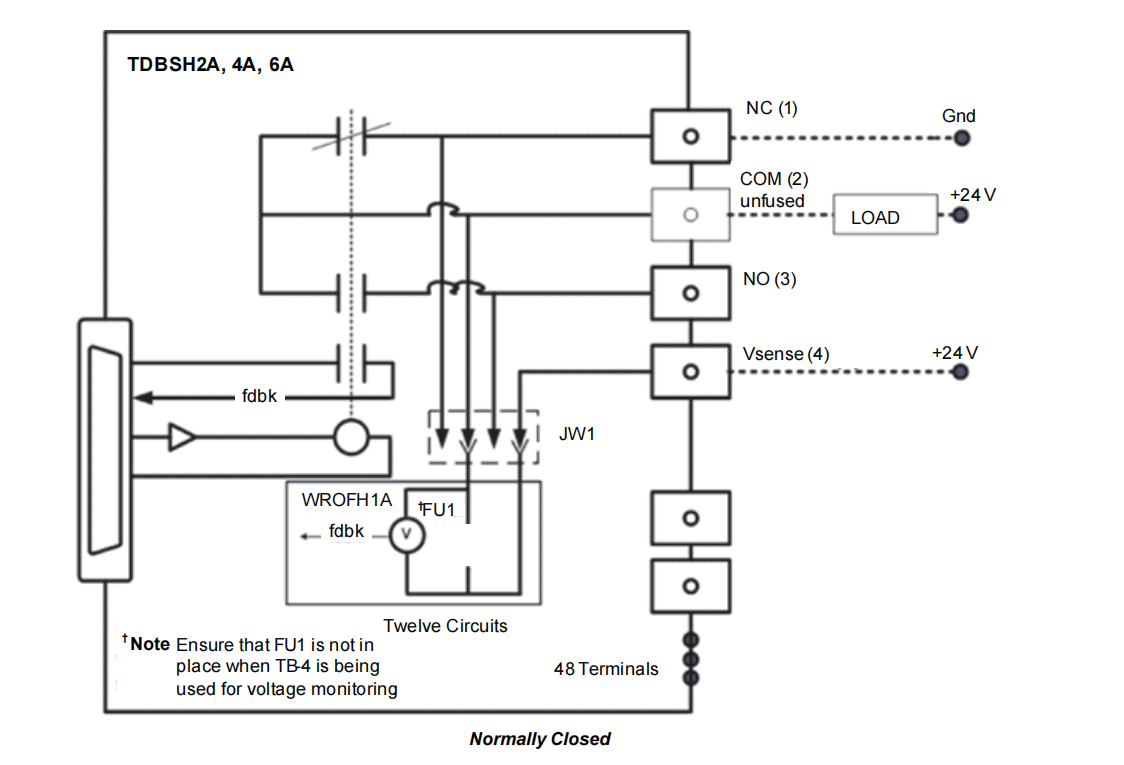
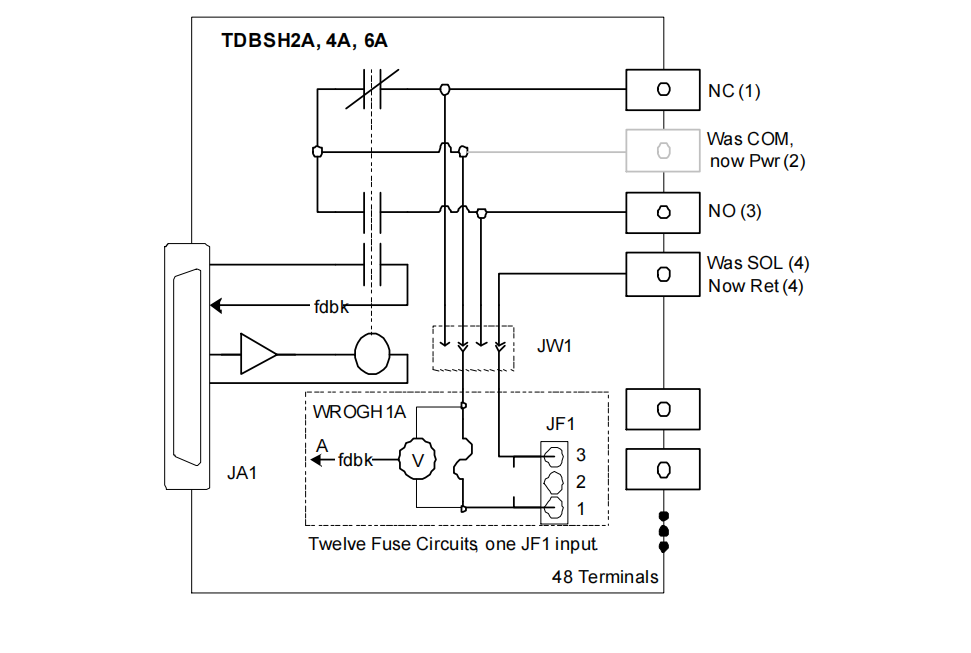
| Wetting Voltage Wiring | Parallel wetting terminals, allows shared leads like H2A | Parallel wetting terminals, allows shared leads | Wiring method is the same, advantageous over the H8A model which requires individual leads. |
| Relay Output Section | Identical to TDBSH2A (12 Form-C relays) | Identical to TDBSH6A (12 Form-C relays) | Output universality is a major advantage of the TDBS series. Model difference does not affect output capability. |
| W-Type Option Board Compatibility | Fully Compatible (WROBH1A, WROFH1A, WROGH1A) | Fully Compatible (WROBH1A, WROFH1A, WROGH1A) | Option board functionality is consistent, providing the same expansion capabilities. |
| Typical Application Scenario | High-voltage switch status monitoring, power system control, interfacing with high-voltage equipment in older plants | Standard PLC/DCS I/O applications, low-voltage sensor and switch interfaces, modern automation equipment | Selection depends on the voltage level of field devices and environmental noise levels. |