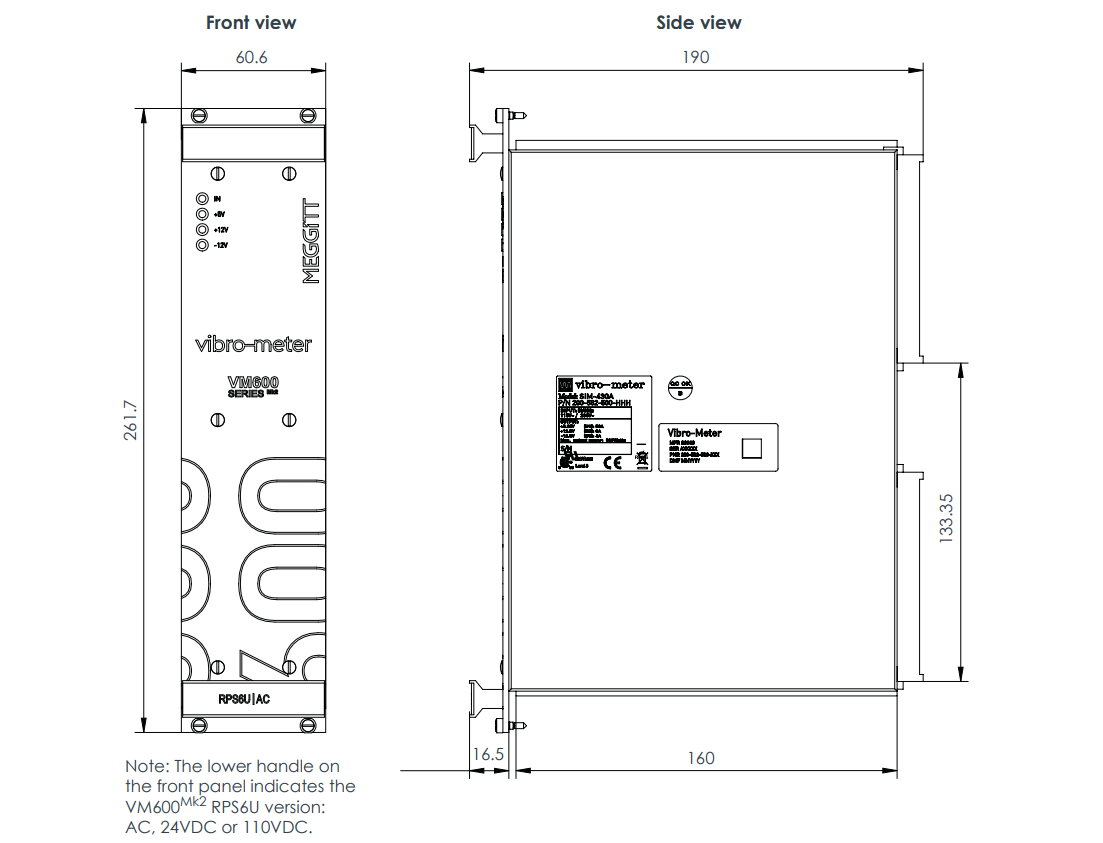
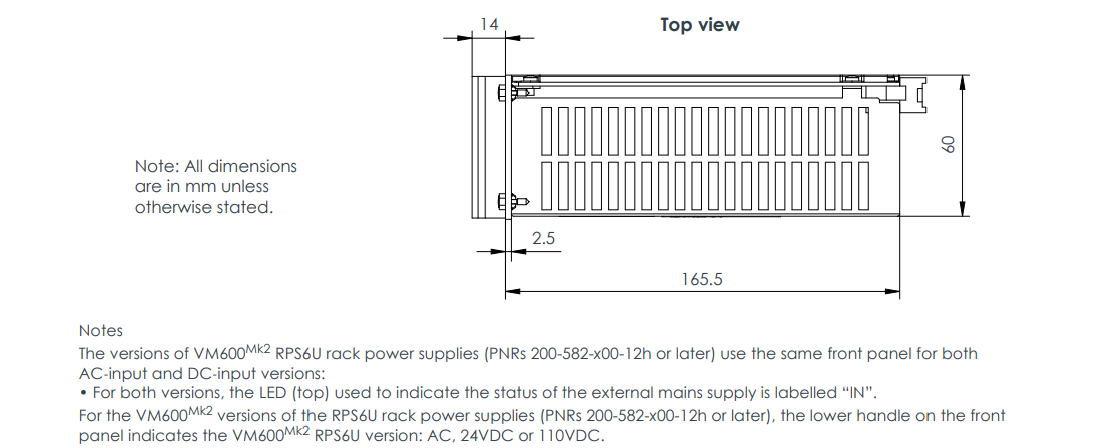
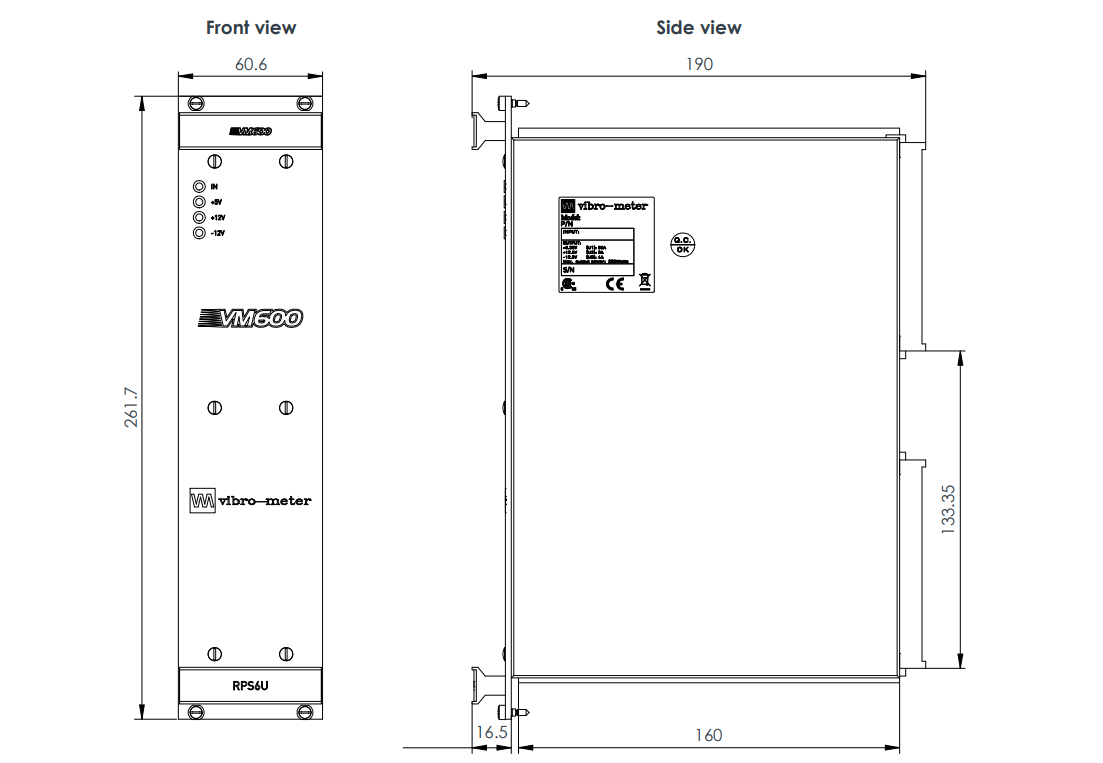
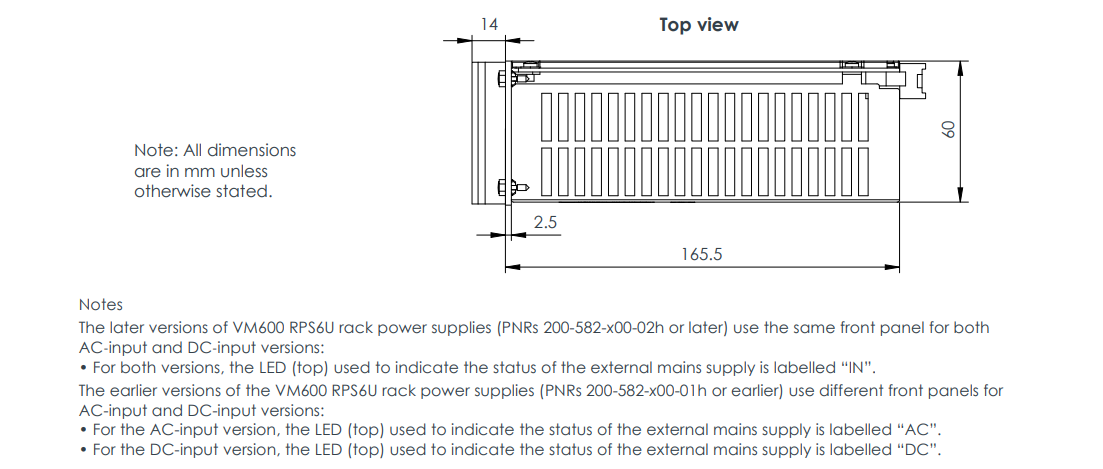
The VM600 RPS6U Rack Power Supply is a core power supply unit from VM product line, specifically designed for the VM600MK2/VM600 series of machinery protection and condition/performance monitoring systems. It is installed in the front of a standard 6U high, 19-inch wide VM600 ABE04x system rack and connects to the rack's backplane VME bus via two high-current connectors, providing stable and reliable +5 VDC and ±12 VDC operating power for the entire rack and all monitoring modules (cards) installed within it.
The RPS6U is the heart that ensures the normal operation of the entire VM600 system. Its design adheres to the philosophy of high performance, high power density, and high efficiency, offering minimal derating across the entire operating temperature range and excellent power output stability. This power supply features output overvoltage, short-circuit, and overload protection, and is equipped with status indicators to display in real-time the status of the external mains supply and various output voltages.
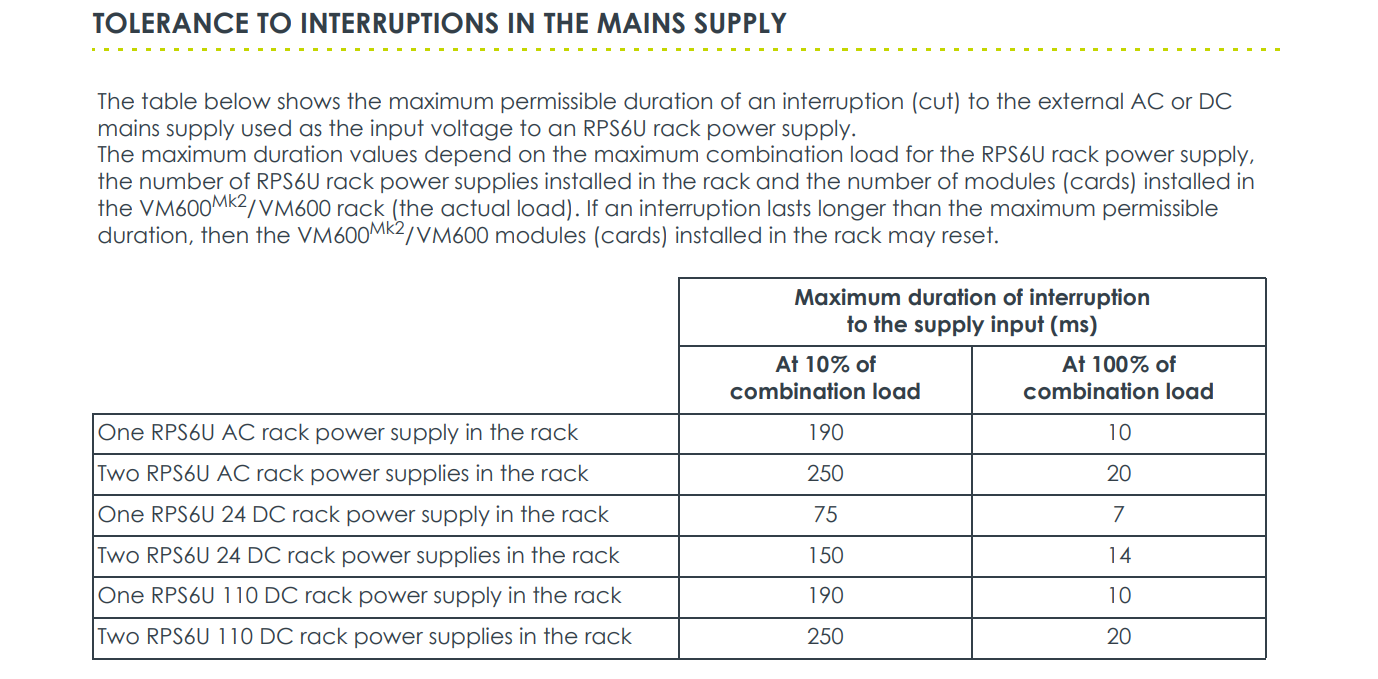
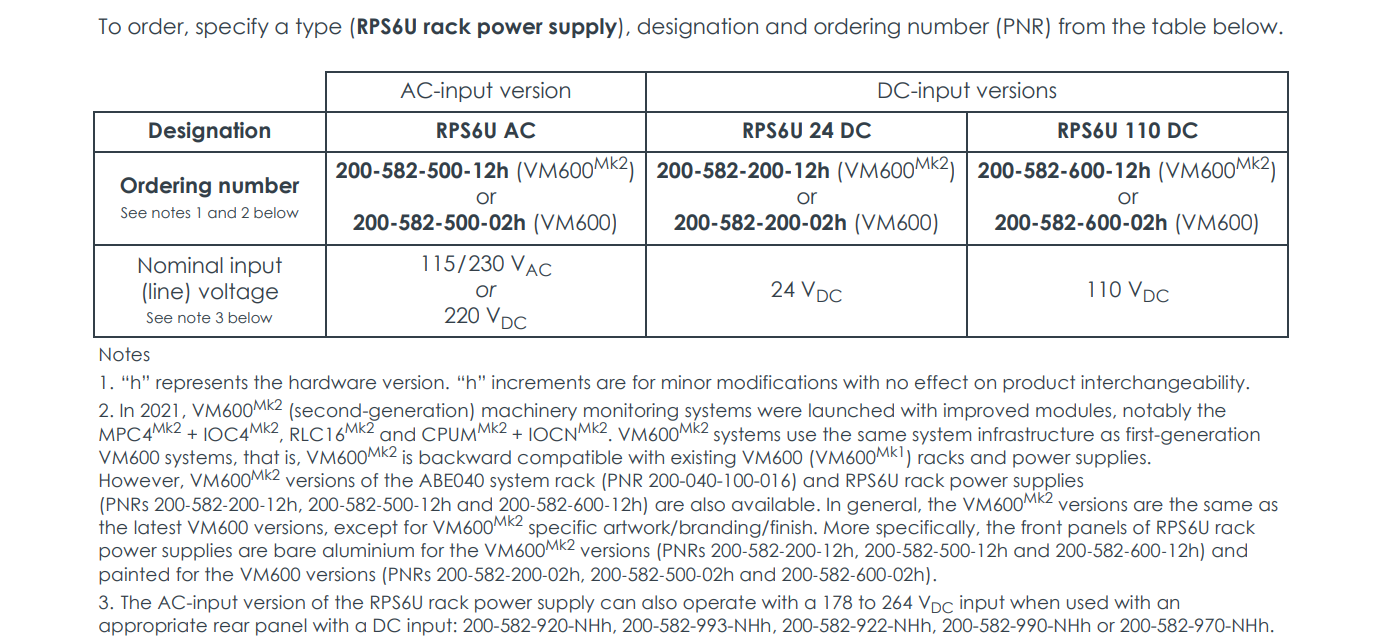
One or two RPS6U power supplies can be installed in a single rack, providing the foundation for redundant configuration, greatly enhancing the availability and reliability of the entire monitoring system. When configured in redundant mode, if one power supply fails, the other immediately takes over the entire load, ensuring continuous rack operation and preventing production interruptions due to power issues. Furthermore, the RPS6U offers multiple versions with AC and DC inputs, enabling flexible adaptation to different industrial site power environments worldwide.
Working Principle
The working principle of the RPS6U rack power supply is a typical embodiment of modern switching power supply technology in critical industrial applications. Its core task is to convert an unstable external AC or DC input power source into the highly stable and clean low-voltage DC power required by the various precision electronic cards within the VM600 system. The process involves power conversion, regulation, protection, and monitoring. The specific principles are as follows:
1. Input Processing and Rectification Filtering
The external mains supply is connected to the RPS6U power supply via an Associated Rear Panel. Depending on the power supply version, the input can be Alternating Current (AC) or Direct Current (DC).
For AC Input Version (RPS6U AC): The input voltage first passes through an Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Filter. This filter suppresses external noise introduced through the power lines and prevents high-frequency switching noise generated inside the power supply from being fed back into the grid, ensuring compliance with EMC standards. Subsequently, the AC is converted into pulsating DC by a bridge rectifier, and then smoothed by large-capacity electrolytic capacitors to form a high-voltage DC bus (typically around 300-400 VDC). This version supports a wide input range (90-132 VAC / 180-264 VAC auto-ranging) and is also compatible with 178-264 VDC input (requires a specific DC input rear panel).
For DC Input Versions (RPS6U 24 DC / RPS6U 110 DC): The DC input voltage is connected directly. The 24VDC version has an input range of 18-32 VDC, and the 110VDC version has an input range of 80-145 VDC. The input DC is also filtered to suppress noise before being sent to the subsequent DC-DC conversion stage. Note that the rear panels usually do not include circuit protection for the DC inputs, so an externally fitted circuit breaker with an appropriate rating is required.
2. High-Frequency Power Conversion (DC-AC-DC)
This is the core of the switching power supply. The rectified and filtered high-voltage DC is fed into the power switching circuit (often using a full-bridge or half-bridge topology). Driven by a Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Controller, this circuit switches the power switches (e.g., MOSFETs or IGBTs) on and off at high frequency (typically tens to hundreds of kHz), converting the high-voltage DC into high-frequency AC square waves.
This high-frequency AC square wave is coupled to the primary winding of a high-frequency transformer. The transformer serves three key purposes here: 1) Electrical Isolation, completely isolating the dangerous input high voltage from the safe output low voltage to meet safety standards; 2) Voltage Transformation, stepping down the high voltage to the required low voltage level; 3) Power Transfer.
3. Output Rectification and Filtering
The high-frequency, low-voltage AC square wave output from the transformer's secondary winding is rectified by Schottky diodes or synchronous rectifiers (higher efficiency) to become pulsating DC again. Subsequently, an LC filter (inductor and capacitor) smoothes it, producing very clean DC output voltages with low ripple and noise (<50 mV p-p): +5 VDC, +12 VDC, and -12 VDC.
4. Feedback and Control Loop (Voltage Regulation)
To ensure extreme output voltage stability, unaffected by input voltage fluctuations and load changes, the RPS6U employs a precise closed-loop feedback control system.
Sampling: The +5V and ±12V outputs are sampled in real-time via a high-precision resistor divider network.
Comparison and Error Amplification: The sampled voltage signal is compared with an internal precision reference voltage (benchmark), generating an error signal.
PWM Modulation: The error signal is sent to the PWM controller, which adjusts the duty cycle of the pulse signal driving the power switches based on the magnitude and direction of the error.
If the output voltage drops slightly due to increased load, the error signal increases, and the PWM controller increases the duty cycle, allowing the power switches to conduct longer, thus transferring more energy to the secondary side, causing the output voltage to rise back to the set value.
Conversely, if the output voltage rises, the duty cycle is reduced.
This dynamic adjustment process is continuous and very fast, ensuring sustained output voltage stability. Its line regulation and load regulation specifications are excellent (<±1% to <±2%).
5. Protection Mechanisms
The RPS6U incorporates multiple protection functions to ensure its own safety and that of downstream loads:
Output Overvoltage Protection (OVP): If the feedback loop fails causing abnormal output voltage rise, the OVP circuit activates immediately, latching off the power output. A restart is required to recover.
Output Overcurrent and Short-Circuit Protection (OCP/SCP): When the output current exceeds safe limits or a short circuit occurs, the protection circuit activates, limiting the output current and automatically recovering after the fault is cleared.
Inrush Current Limiting: At startup, a Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) thermistor or dedicated control circuit limits the inrush current charging the input capacitors, preventing damage to rectifier components and circuit breaker tripping.
6. Redundancy and Parallel Operation Principle
When two RPS6U power supplies are installed in a rack, they work in parallel via the backplane to power the load. Their operating mode is determined by the system configuration:
Redundant Mode (N+1): Both power supplies are operational and share the load current. Special current sharing circuitry ensures the output currents of both supplies are basically equal. If one fails, its output is isolated, and the other immediately assumes 100% of the load, achieving seamless switching without affecting system power. In this mode, the system's maximum available current is limited by the capability of a single supply.
Non-Redundant Mode (N+N): Both power supplies work together to provide greater total output power, typically used when environmental temperatures above 50°C require derating. Here, both supplies share the load, but the load distribution may not be perfectly balanced (up to a 20:80 ratio). The total available current is about 125% of a single supply. In this mode, failure of any one power supply will cause system power loss or performance degradation.
7. Status Monitoring and Communication
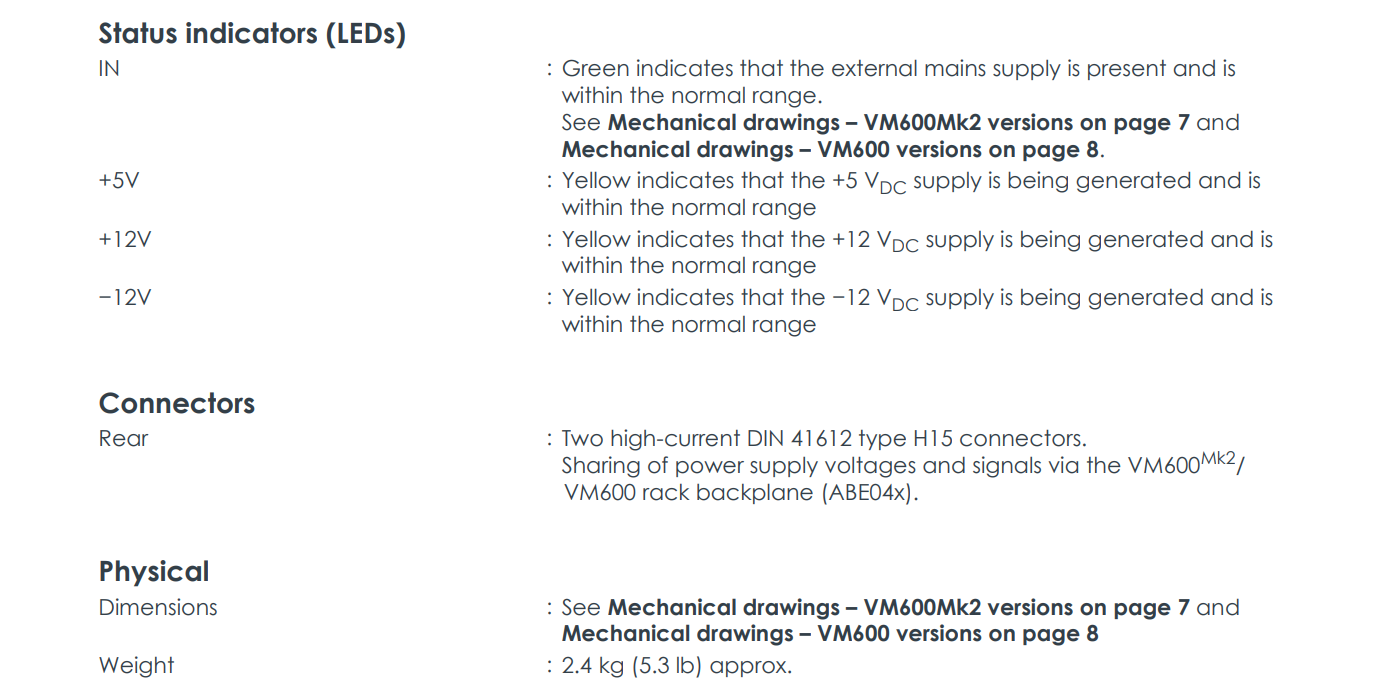
LED status indicators (IN, +5V, +12V, -12V) on the front panel provide users with intuitive power status. Additionally, the "OK" status of the power supply is output as a dry contact signal via a power supply check relay at the rear of the rack, which can be acquired by superior monitoring system for remote monitoring.
Core Features and Benefits
High Power Output: Maximum output power of 330 W (later versions), providing ample power for a fully loaded rack of cards.
Multiple Input Types: Offers AC (115/230VAC) and DC (24VDC/110VDC) input versions to adapt to different industrial power standards worldwide.
Supports Redundant Configuration: Allows installation of dual power supplies for N+1 redundancy, significantly improving system reliability and availability.
Excellent Electrical Performance: High efficiency (83%-85%), low ripple and noise, excellent line and load regulation.
Comprehensive Protection Features: Includes overvoltage, overcurrent, and short-circuit protection, with auto-recovery after short-circuit.
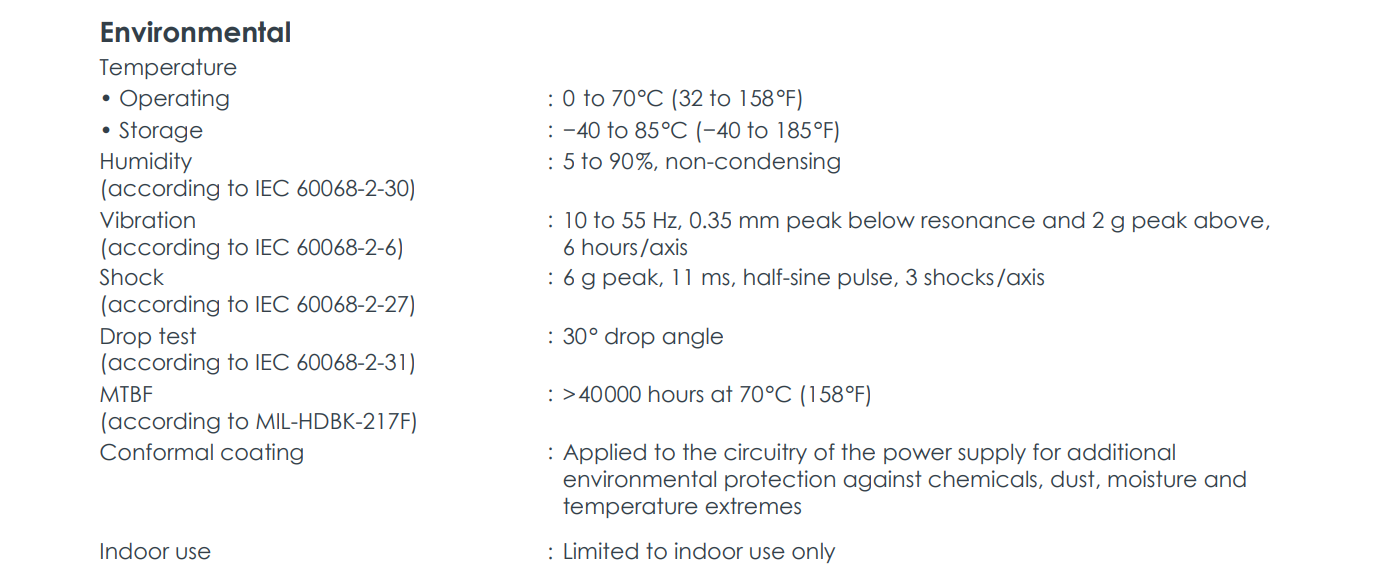
Wide Operating Temperature Range: 0 to 70°C, can handle high-temperature environments with derating curves or forced air cooling.
Clear Status Indication: Front panel LEDs display real-time status of input power and output voltages.
Hot-Swap Support (depends on rack design): Allows replacement of power modules without system power-down.
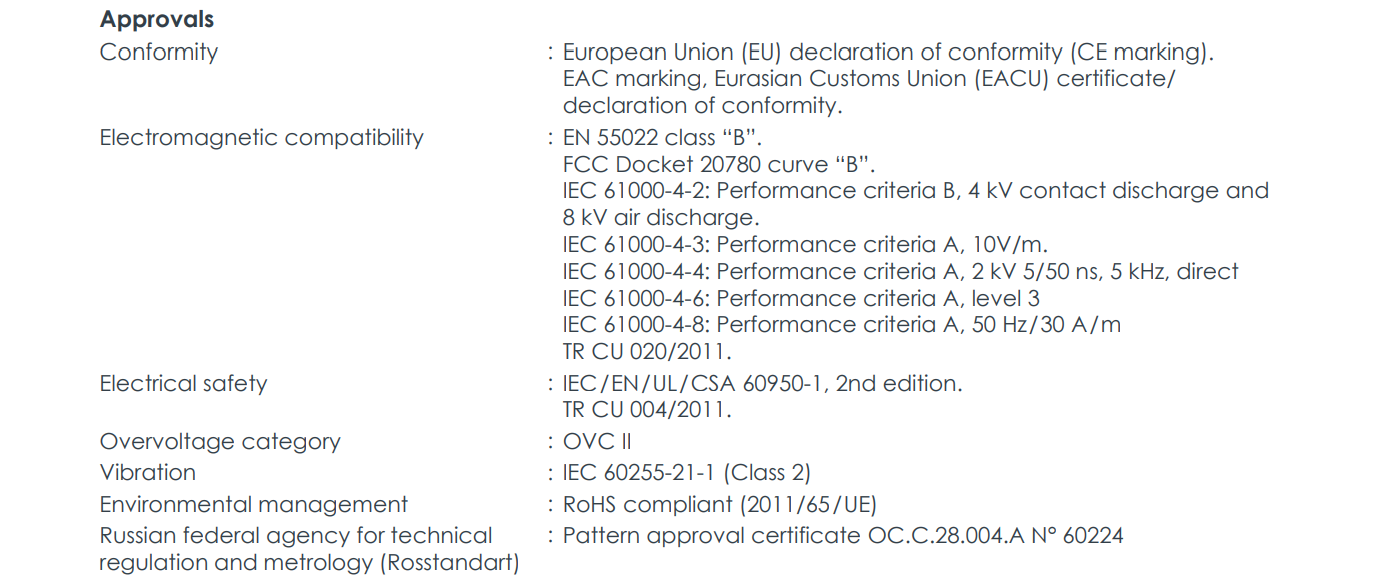
Complies with International Standards: CE, EAC certified, meets EMC, electrical safety, and other requirements.
Detailed Comparison of Different RPS6U Versions
RPS6U power supplies differ primarily in three dimensions: Input Type, Output Power, and System Generation (VM600 vs VM600 Mk2). Below is a detailed comparison:
1. Comparison by Input Type and Electrical Parameters
This is the core differentiator, determining the power supply's application scenario.
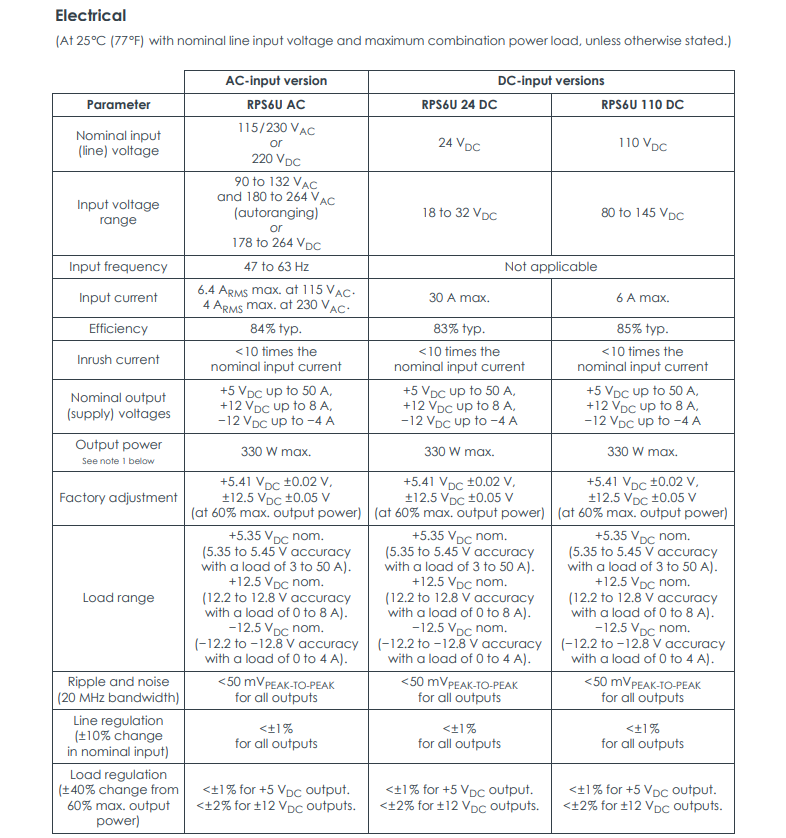
| Parameter | RPS6U AC (AC Input Version) | RPS6U 24 DC (DC Input Version) | RPS6U 110 DC (DC Input Version) |
| Nominal Input Voltage | 115/230 VAC or 220 VDC | 24 VDC | 110 VDC |
| Input Voltage Range | 90-132 VAC / 180-264 VAC (Auto-ranging)
or 178-264 VDC | 18 - 32 VDC | 80 - 145 VDC |
| Input Frequency | 47 - 63 Hz | Not Applicable | Not Applicable |
| Max Input Current | 6.4 A RMS @115VAC
4 A RMS @230VAC | 30 A max | 6 A max |
| Typical Efficiency | 84% | 83% | 85% |
| Application Scenario | Standard industrial grid applications | Common DC control panel, battery backup applications | Specific industrial DC power applications |
| Rear Panel Requirement | Requires AC input rear panel (with fuse, filter) | Requires DC input rear panel | Requires DC input rear panel |
| External Protection | Fuse included on rear panel | External circuit breaker required | External circuit breaker required |
| Ordering Number (PNR) VM600 | 200-582-500-02h | 200-582-200-02h | 200-582-600-02h |
| Ordering Number (PNR) VM600 Mk2 | 200-582-500-12h | 200-582-200-12h | 200-582-600-12h |
Key Differences Summary:
Input Flexibility: The AC version is the most flexible, compatible with global AC voltages and DC input. DC versions are designed for specific DC voltages.
Accessories and Protection: AC version rear panels are more integrated with built-in protection; DC versions require extra attention to external circuit protection.
Application Field: AC version is the most universal; 24DC version is common where battery backup is needed; 110DC version is for specific industrial environments.
2. Comparison by Output Power and Version Iteration
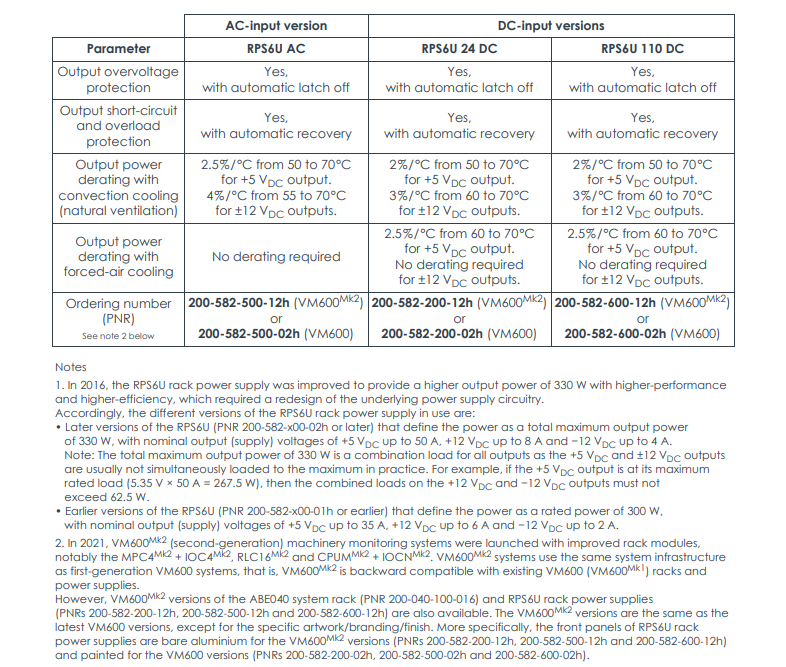
The RPS6U underwent a major upgrade in 2016, improving output power and performance.
| Parameter | Later Version (Post-2016) | Earlier Version (Pre-2016) |
| Identifier | PNR ending with -02h or higher (VM600)
PNR ending with -12h or higher (VM600 Mk2) | PNR ending with -01h or lower |
| Max Output Power | 330 W | 300 W |
| +5 VDC Output | Up to 50 A | Up to 35 A |
| +12 VDC Output | Up to 8 A | Up to 6 A |
| -12 VDC Output | Up to -4 A | Up to -2 A |
| Core Difference | Internal power circuitry redesigned for higher power density and efficiency. | Relatively lower output capability. |
Key Differences Summary: The 330W version provides stronger power capability, able to support denser or higher-power consumption card configurations, and is the preferred choice for current and future systems. The 300W version is primarily for maintaining existing older systems.
3. Comparison by System Generation (VM600 vs VM600 Mk2)
VM600 Mk2 is the second-generation system, fully compatible with the first-generation VM600, but some components have slight cosmetic differences.
| Characteristic | VM600 Mk2 Version | VM600 (1st Gen) Version |
| Ordering Number (PNR) | 200-582-xxx-12h | 200-582-xxx-02h |
| Front Panel Material | Bare Aluminium | Painted |
| System Compatibility | Fully backward compatible, can be used in VM600 racks | Can be used in VM600 racks |
| Performance & Function | Identical | Identical |
Key Differences Summary: The Mk2 and first-generation versions of the RPS6U are identical in electrical performance, functionality, and mechanical interface. The only difference is the surface finish of the front panel. The Mk2 version uses a bare aluminium appearance to distinguish it from the first-generation product for visual identification. Both can be mixed and used in the same system.
Selection Advice
Determine Input Type: Choose AC or DC input version based on the power source available on-site. The AC version is the most universal.
Confirm Power Requirement: Always choose the 330W later version (PNR suffix -02h or -12h) for the best power margin and system compatibility.
Consider Redundancy: For critical applications, strongly recommend configuring two power supplies for redundancy, significantly improving system availability.
Match the Rear Panel: Select the correct associated rear panel (e.g., F910, F920, F993, etc.) based on the chosen power input type. Note that DC input versions require an external circuit breaker.
Note Generation Appearance: If seeking a unified system appearance, the VM600 Mk2 system should choose the Mk2 version power supply (-12h) with the bare aluminium front panel.