The UNS 0868 Power Supply Unit serves as the core component responsible for power supply and management within the ABB UNITROL® F series excitation systems, rightfully regarded as the "heart" of the entire control system. Its primary design objective is to provide highly reliable, redundant, and stable DC operating power for the control electronics of the excitation system. This ensures the continuous and uninterrupted operation of all regulation, control, and protection functions under various generator operating conditions, including start-up, shutdown, and even transient events such as grid faults.
Within the excitation system, control electronics (such as the SDCS-CON-2 control board, UNS 1860 signal processing device, UNS 0863 I/O interface, etc.) require clean, stable DC voltages. However, the voltage levels and quality of power sources available in industrial settings (such as station batteries and auxiliary AC power) often do not meet these requirements. The UNS 0868 is designed specifically to address this issue, fulfilling the critical roles of power adaptation, redundancy switching, and electrical isolation. Its core design philosophy centers on availability and safety. By incorporating dual power inputs and an N+1 redundancy concept, it prevents a single power source failure from causing a complete shutdown of the excitation control system, thereby safeguarding the generator and the power grid.
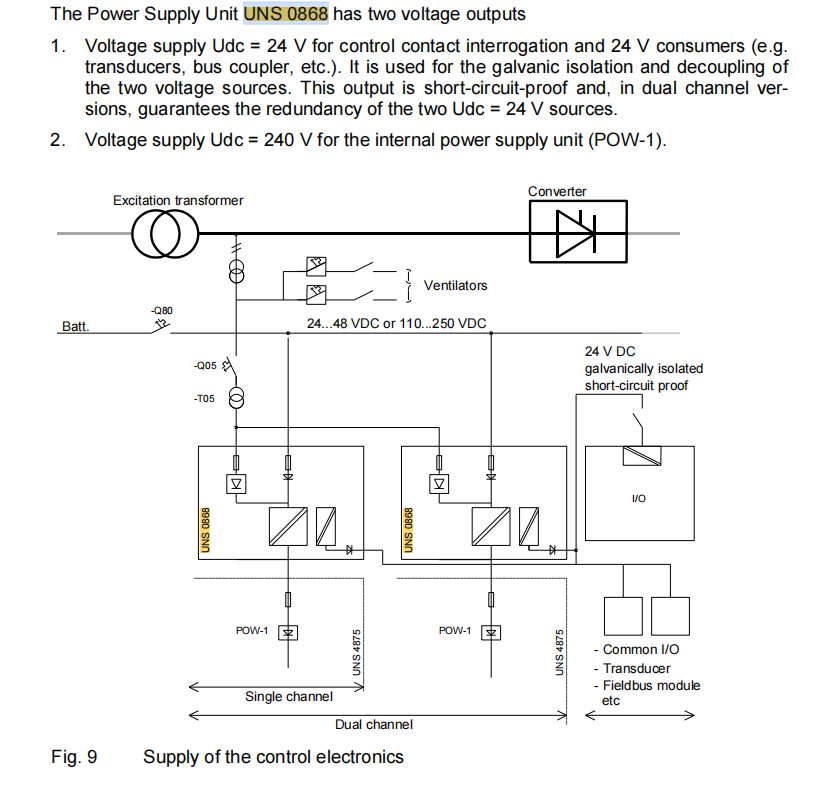
This unit is a standalone "board-mounted" device installed within the excitation cabinet, connected to external batteries, AC power sources, and internal loads via standard terminal blocks.
2. Key Features
The functions of the UNS 0868 are comprehensively centered around power conversion, distribution, and management, specifically manifested in the following aspects:
2.1. Dual Redundant Power Inputs
Input Channels: Provides two independent power input channels.
DC Input: Connects to the power station's battery bank. This is the primary and most reliable power source for the system.
AC Input: Connects to the secondary side of the excitation transformer or the plant auxiliary AC power supply. This source serves as a backup or supplement to the battery.
Automatic Seamless Switching: The two inputs are decoupled internally via diodes. As long as any one of the power sources is normal, the unit's output is guaranteed to be maintained, enabling true seamless switching and eliminating a single point of failure.
2.2. Multiple Stable DC Voltage Outputs
The UNS 0868 generates two independent DC outputs with different characteristics to power different parts of the system:
240 VDC Main Output: This output is specifically designed for the SDCS-POW-4 power supply board installed inside the main UNITROL® F unit. The POW-4 board, in turn, generates the various low-level DC voltages required by the control system (e.g., ±15V, +5V, +24V). This output is the ultimate energy source for the control logic and signal processing.
24 VDC Auxiliary Output: This is a galvanically isolated 24V DC voltage, specifically used as:
Interrogation Voltage: Provides the common potential for the 16 digital input circuits on the UNS 0863 I/O Interface.
General-Purpose Supply: Powers other 24V consumers, such as transducers, bus couplers, etc.
2.3. Comprehensive Power Monitoring and Status Indication
Input Voltage Monitoring: The unit continuously monitors the status of both the DC and AC input voltages.
Fail Signal Output: When either input voltage fails, the unit provides an alarm signal via a relay fault contact (FAIL signal). This signal can be acquired by the supervisory control system to alert operational staff about the power status.
LED Status Indication: AC ON and DC ON LED indicators on the front panel provide a visual display of the presence status of the two input power sources.
2.4. Support for Parallel Redundant Operation
24V Output Paralleling: In dual-channel (AFT) excitation systems, the 24V DC outputs of two UNS 0868 units are allowed to be connected in parallel. The unit incorporates decoupling diodes for this purpose and provides dedicated paralleling terminals (6/7 and 8/9), ensuring that if one power unit fails completely, the other can seamlessly take over the entire 24V load, achieving N+1 redundancy at the power supply level.
2.5. Hold-up and Buffering
External Capacitor Interface: The 240V DC output is designed with terminals (18/20) for connecting an external capacitor. This allows the energy stored in the capacitor to maintain the 240V DC output during brief interruptions of the DC input power (e.g., milliseconds to hundreds of milliseconds), ensuring the control system does not reset or malfunction due to instantaneous power dips. Its sustaining capability is measured as 2.2 mF/s, and the capacitor value can be selected based on the system's required hold-up time.
3. Working Principle and Signal Processing Mechanism
The internal operation of the UNS 0868 involves a sophisticated process of power conversion and control. The following sections delve into its complete working principle from input to output.
3.1. Dual Input Processing and Redundancy Switching Mechanism
a. Input Reception and Range Adaptation:
The UNS 0868 comes in two versions to accommodate different global power station standards:
Version 1: For 24/48 VDC systems and 34 VAC systems.
Version 2: For 110/250 VDC systems and 170 VAC systems.
The internal circuitry, particularly the front-end converter, is designed to automatically adapt to the wide input voltage range specified for its version.
b. Diode Decoupling and "OR" Logic:
This is the core of the redundancy implementation. The DC input and AC input are combined before entering the subsequent switching converter, each through its dedicated diode. These two diodes form a simple "OR" logic gate:
If the DC input is normal, current flows from the DC side.
If the DC input is lost but the AC input is normal, current flows from the AC side.
The diodes prevent current from flowing back from one source into the other faulty source, achieving perfect electrical isolation and non-circulating current switching. This process is implemented purely in hardware, is extremely fast (microseconds), and has no switching delay.
3.2. DC-DC Boost Conversion Principle
a. High-Frequency Switching Conversion:
Regardless of whether the energy comes from the DC or AC input (AC is first rectified to DC), the combined DC power is not used directly. It is fed into a high-frequency switching DC-DC boost converter. The core of this converter is a high-speed switching transistor (e.g., MOSFET) that turns on and off repeatedly at a high frequency (typically tens to hundreds of kHz).
b. Energy Storage and Release:
When the switch is on, energy is stored in an inductor. When the switch turns off, the inductor, to maintain its current, generates a counter-electromotive force. This voltage adds to the input voltage, producing a pulse higher than the input voltage.
c. Rectification and Filtering:
This high-frequency, high-voltage pulse passes through a high-frequency transformer (providing isolation) and a rectifier diode, and is then smoothed by an output capacitor, ultimately yielding a stable 240 VDC output voltage. A precise feedback control loop (PWM modulation) ensures that the output voltage remains stable at 240V ±10%, regardless of fluctuations within the allowed input voltage range.
3.3. 24V Isolated Output Generation Principle
The 240V DC bus voltage is further processed to generate the 24V output. This process is typically handled by another, independent DC-DC converter, whose core is also a high-frequency switching circuit.
Galvanic Isolation: The high-frequency transformer in this converter is isolated, meaning its primary (240V side) and secondary (24V side) are electrically completely separate. This is crucial as it breaks the electrical connection between the control circuits (24V side) and the main power circuits (240V side), significantly enhancing the system's noise immunity and safety by preventing issues caused by ground potential differences.
Regulation and Current Limiting: This circuit also features voltage regulation to ensure stable 24V output. Furthermore, it is designed to be short-circuit proof, meaning that even if the output terminals are accidentally short-circuited, the circuit will enter a current-limiting mode or shut down, automatically recovering once the fault is cleared, without causing damage to the unit.
3.4. Monitoring Circuit Working Principle
a. Voltage Sensing:
The unit contains voltage comparator circuits that continuously sample the DC and AC input voltages.
b. Logic Judgment and Signal Output:
Status LEDs: When the sampled voltage exceeds a certain set threshold, the comparator drives the corresponding AC ON or DC ON LED to illuminate.
FAIL Signal: The monitoring logic is designed such that: the FAIL signal is activated (contacts open) only when both input voltages fail simultaneously. If only one input fails, the FAIL signal does not activate because the other can still maintain operation. This avoids unnecessary false alarms. The FAIL signal is provided by a relay contact output, offering a passive, potential-free, and isolated fault indication method that can be safely connected to any external monitoring system.
3.5. Protection Mechanisms
Input Fuses: The unit incorporates fuses (F1, F2) on both the AC and DC input sides internally. These serve to quickly disconnect the power source in the event of a severe internal fault (e.g., switching transistor short-circuit), preventing fault escalation and protecting the upstream batteries and distribution system.
Undervoltage Lockout: In the 'b' version, the unit features an undervoltage lockout function. It inhibits the converter from starting or operating when the input voltage is too low, preventing potential damage from operation under abnormal voltage conditions.
4. System Integration and Configuration
4.1. Electrical Connections
Input Terminals:
Terminals 1(L), 2(N): Connect to AC input.
Terminals 4(-), 5(+): Connect to DC input (observe polarity).
Output Terminals:
Terminals 17(+), 19(-): Output 240 VDC to the POW-4 power supply board.
Terminals 6(+), 8(-): Output 24 VDC interrogation voltage.
Terminals 7, 9: Used for paralleling the 24V outputs.
Signal Terminal:
4.2. Application Architecture within the Excitation System
In a typical UNITROL® F system, the 240V DC output of the UNS 0868 is connected directly to the input of the SDCS-POW-4 power supply board inside the main control unit. The POW-4 board then provides various level operating voltages via flat cables to the SDCS-CON-2 control board, UNS 1860 signal processing device, etc. The 24V DC output is connected to the UNS 0863 I/O Interface to power its digital inputs and internal relays.
4.3. Commissioning and Function Check
Version Confirmation: First, confirm that the UNS 0868 version (V1 or V2) matches the site's battery and auxiliary AC voltages.
Power-On Check: After applying power, observe whether the AC ON and DC ON LED indicators illuminate.
Voltage Measurement: Use a multimeter to measure the 240V DC output (terminals 17/19) and the 24V DC output (terminals 6/8); voltages should be within the allowed tolerance.
Fault Simulation: Disconnect one input power source and observe if the other can seamlessly maintain the output, and verify the status of the FAIL signal.
5. Application Scenarios
The UNS 0868 is designed for industrial environments requiring high reliability, primarily used in:
Power Plant Excitation Systems: UNITROL® F excitation cabinets in various types of power plants (thermal, hydro, nuclear, gas turbine, etc.).
Critical Industrial Processes: Critical processes driven by large synchronous motors, such as in chemical plants, compressed air energy storage, and metallurgy.
Marine Power Systems: Excitation control for marine generators.
Any control system requiring high availability and redundant power supply assurance.