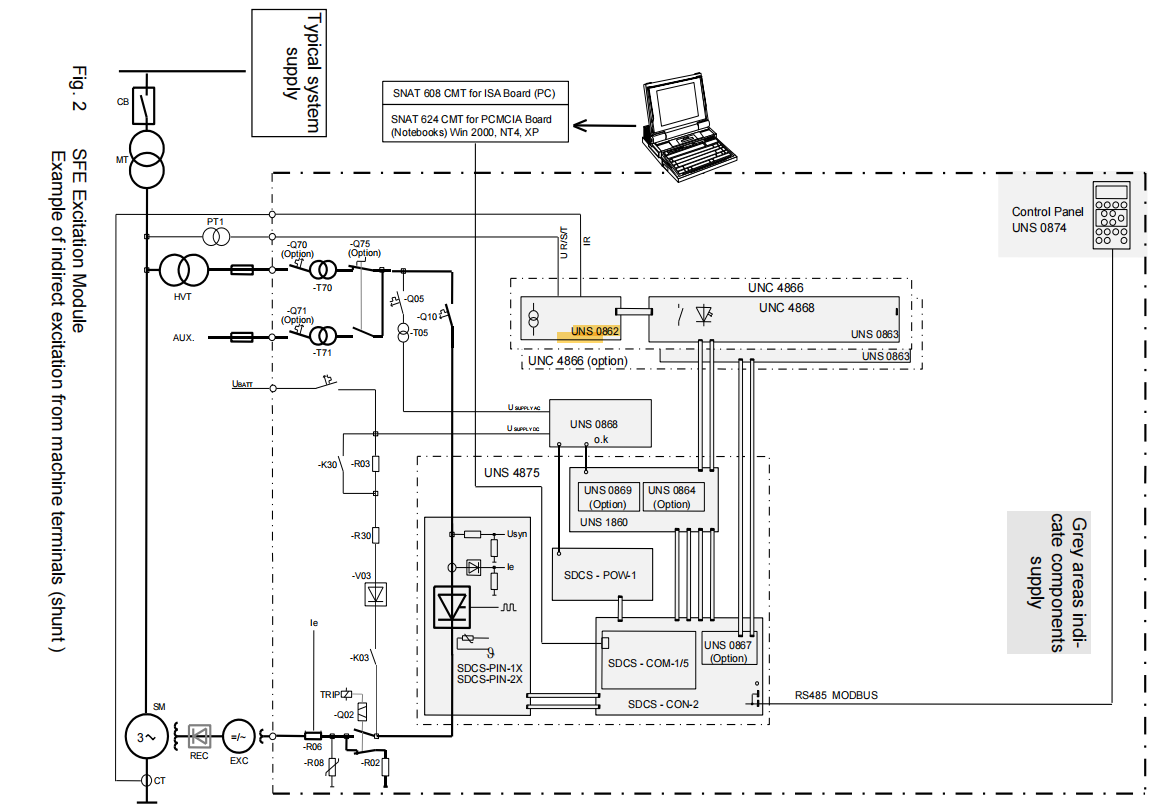
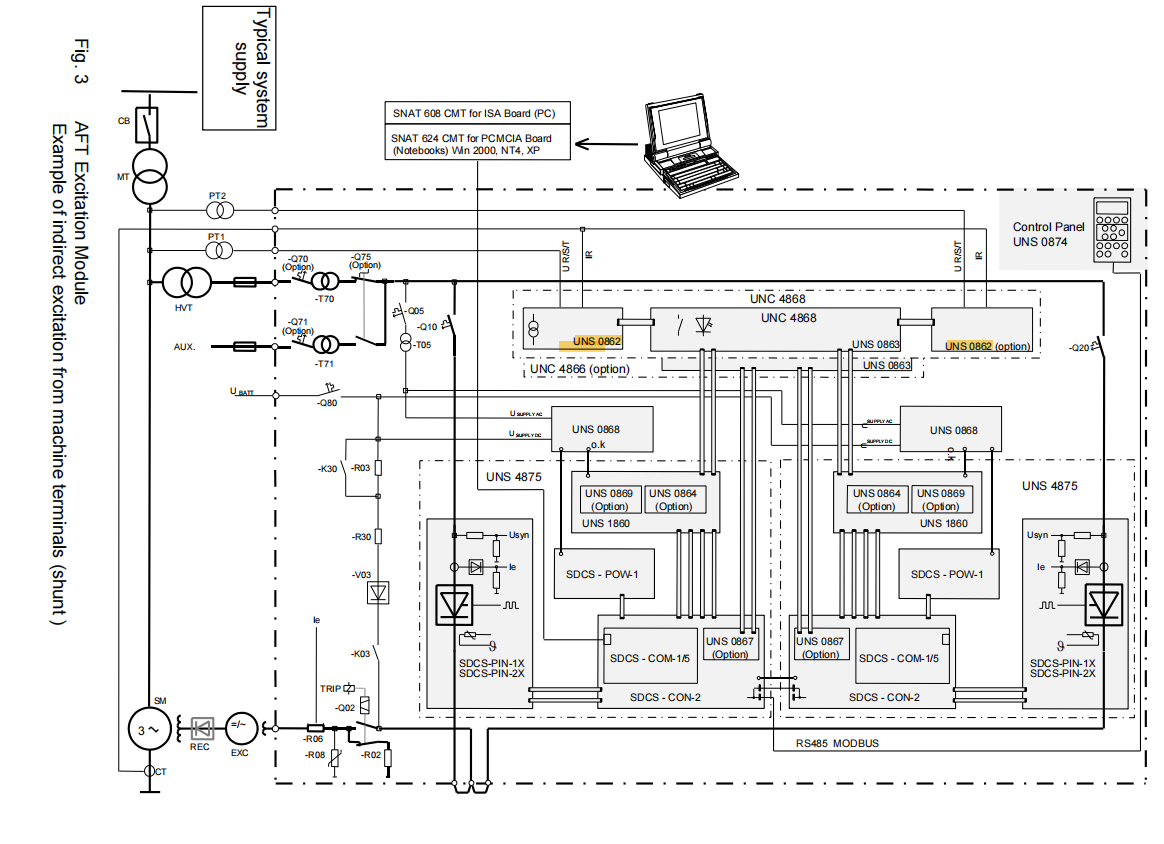
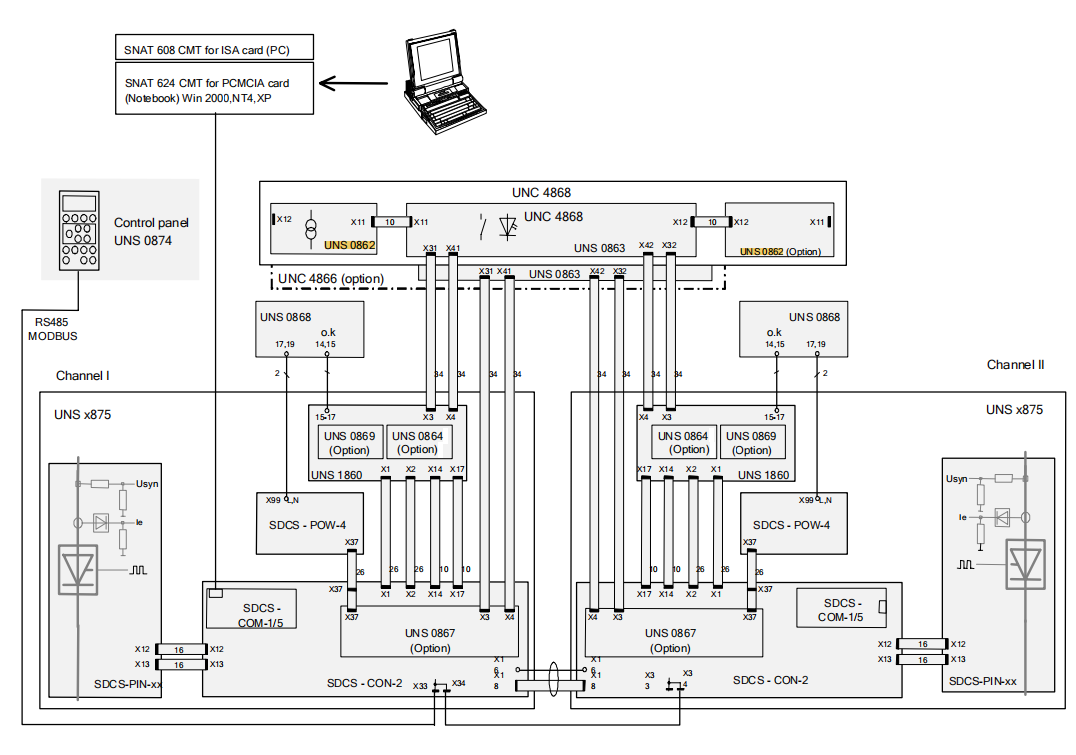
The UNS 0862 AC Actual Value Measurement Interface is a crucial front-end signal acquisition device in the ABB UNITROL® F series excitation systems. Its core mission is to accurately and safely acquire the operating status parameters of synchronous machines—namely, the three-phase machine voltage and single-phase current—and convert them into standardized low-voltage signals that can be processed by the subsequent electronic control system.
In an excitation system, the Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR) requires real-time and precise access to the generator's terminal voltage and load current to make correct control decisions, maintain grid voltage stability, and reasonably distribute reactive power. The UNS 0862 is the key link enabling this "sensing" function. As the starting point of the signal chain, its measurement accuracy and reliability directly impact the stable operation of the entire excitation system, and even the generator and the power grid.
This module is designed as a standalone board card and is closely connected to the I/O Interface UNS 0863 via pre-fabricated flat cables, together forming a standardized, high-impedance interface between the excitation system and external voltage and current transformers.
2. Key Features
The functionality of the UNS 0862 is highly specialized, primarily embodied in the following two aspects:
2.1. Three-Phase Machine Voltage Measurement
Number of Channels: 3 phases (UR, US, UT).
Galvanic Isolation: Achieved through two dedicated internal measurement transformers (connected in a V-connection), providing complete galvanic isolation between the high-voltage side (transformer secondary) and the low-voltage side (control system electronics). This is a vital safety measure, preventing high voltages from the power system from entering the low-voltage control circuits, which could damage expensive control equipment and endanger personnel.
Signal Transformation: Precisely scales down the standard secondary voltages from Voltage Transformers (VTs) (typically 100V, 110V, or 120V) to a safe level suitable for electronic circuitry—5 V AC RMS.
High Linearity: Maintains excellent linear characteristics up to 130% of the rated value, with an instantaneous overload capability of 150%, ensuring undistorted signals even during system transients.
2.2. Single-Phase Machine Current Measurement
Number of Channels: 1 phase (typically measuring R-phase current IR).
Galvanic Isolation: Similarly achieved through a dedicated current measurement transformer.
Signal Transformation & Conversion: Converts the standard secondary current from Current Transformers (CTs) (1A or 5A) into a proportional voltage signal. In the standard configuration, the rated input current corresponds to an output voltage of 3 V AC RMS. This is achieved by connecting a precision burden resistor across the transformer's secondary.
2.3. Signal Distribution & Interface
3. Working Principle and Signal Processing Mechanism
The operating principle of the UNS 0862 is based on classical electromagnetic induction and Ohm's law. Its internal signal processing flow is clear and precise. The following sections delve into its operational mechanism.
3.1. Machine Voltage Measurement Principle
a. Input & Isolation:
The three-phase secondary voltages from the machine terminal voltage transformers (e.g., 110V AC) are connected to the input terminals of the UNS 0862. These three-phase voltages are immediately fed into two specially designed, high-precision measurement transformers. This V-connection (or "open-delta" connection) method effectively measures the three-phase voltages using the minimum number of components.
b. Ratio Transformation:
The transformation ratio of these transformers is carefully designed. For instance, with a primary input of 110V, the secondary will precisely output 5V. This process achieves two core objectives:
Voltage Level Conversion: Steps down the high-voltage signal to a safe low-voltage signal.
Galvanic Isolation: Establishes a safety barrier, isolating the ground of the control system from the ground of the power system, effectively suppressing ground loop interference and common-mode noise.
c. Output Drive:
The transformed low-voltage signals (UR, US, UT, each 5V RMS) are directly sent to the output connectors X11 and X12. These signals are unrectified AC signals, preserving the voltage's phase and frequency information, which is crucial for subsequent calculations of frequency, active power, and reactive power in the UNS 1860 Signal Processing Device.
3.2. Machine Current Measurement Principle
a. Input & Isolation:
The secondary current from the current transformer (1A or 5A) flows into the current measurement channel of the UNS 0862. This current passes through the primary side of a high-precision current measurement transformer.
b. Current-to-Voltage Conversion:
This is the key step in current measurement. A precision burden network, consisting of a fixed resistor R1001 (factory set to 330Ω) and a permanently soldered 3.3kΩ parallel resistor, is connected across the transformer's secondary. According to Ohm's Law (V = I × R), the current flowing through this burden resistor produces a proportional voltage drop.
Total Burden Calculation: In the standard configuration, the total burden resistance R_load = 1 / (1/3300 + 1/330) ≈ 300Ω.
Rated Output: The design goal is for the rated input current (1A or 5A) to produce a voltage of 3 V AC RMS across the burden resistor. This means the transformer's turns ratio and the burden resistor are co-designed. For example, for a 5A input, the transformer might have a higher ratio, resulting in a smaller secondary current that still produces 3V across the 300Ω burden.
c. Output & Configuration Flexibility:
The resulting 3V RMS voltage signal is sent to the output connectors. This design allows for adaptation to different application scenarios or customized signal amplitude requirements by replacing or adjusting the burden resistor R1001, offering good engineering flexibility.
3.3. Accuracy and Reliability Design
Linearity: All transformers use high-quality cores and winding techniques to ensure good linearity across a wide range from zero to 150% of the rated value, preventing signal distortion.
Low Power Consumption: Each voltage channel consumes less than 0.5 VA, and the current channel also consumes less than 0.5 VA. This reduces the burden on the voltage and current transformers, helping to maintain high accuracy for the entire measurement system.
Connection Reliability: The input side uses 4mm² double spring-clamp terminals, allowing the connection of two conductors (wire or strand), ensuring secure and reliable connections, which is particularly important for preventing open circuits in current loops.
4. System Integration and Configuration
4.1. Mechanical and Electrical Installation
The module is secured in place via mounting bolts.
Voltage and current input signals are connected via 4mm² double spring-clamp terminals, providing robust connections suitable for power application environments.
4.2. Connection to Other System Parts
To UNS 0863: Connected using a 10-pin flat cable (supplied with the UNS 0862, e.g., type HIEE 405181 P1) to the X11 and/or X12 ports of the UNS 0863 I/O Interface.
Signal Path: The acquired voltage and current signals are forwarded via the UNS 0863 to the UNS 1860 Signal Processing Device, where they undergo further processing like rectification, filtering, and calculation (e.g., power, frequency), ultimately for use by the microprocessor on the SDCS-CON-2 control board.
4.3. Configuration and Adjustment
Burden Resistor Adjustment: Although R1001 is set to 330Ω ex-works, it can be replaced if needed to change current measurement sensitivity or adapt to special CTs, based on the formula V_out = I_primary * (Total Resistance of Burden Network). The replacement resistor must comply with the ABB standard XN 400323 and must not exceed a maximum power dissipation of 0.33W.
Dual-Channel System Configuration: In AFT dual-channel systems requiring the highest reliability, if two independent sets of machine voltage and current transformers are equipped, then two UNS 0862 devices are needed. One device's X11 connects to UNS 0863's X11 (Channel I), and the other device's X11 (or X12) connects to UNS 0863's X12 (Channel II). In this case, the TWIN jumper on the UNS 0863 must be set to "Y" to inform the system of the presence of two independent measurement sources.
5. Application Scenarios
The UNS 0862 is a standard component of the UNITROL® F excitation system, widely used in all applications employing this series:
Large Thermal Power Plants: For monitoring the terminal voltage and current of turbo-generators, providing core feedback signals for the AVR.
Hydroelectric Power Stations: For excitation control of hydro-generators, adapting to potentially more frequent changes in operating conditions.
Industrial Drives & Large Synchronous Motors: In drive applications such as compressors and pumps, ensuring stable motor operation and power factor correction.
Marine Power Systems: Providing reliable measurements for the excitation control of marine generators.
Any Grid-Connected or Islanded Power Generation System with High Requirements for Grid Stability.