The DS200TCPSG1A is a critical power supply module within General Electric's Speedtronic™ Mark V Turbine Control System. It is typically installed in various control panel cores (e.g., <R>, <S>, <T>, <C>, <P>) and is responsible for providing stable and reliable DC power to printed circuit boards (e.g., DCCA, LCC, TCDA, TCEA). This power module is fundamental to the Mark V system's high availability, fault tolerance, and online maintenance capabilities.
The Mark V control system is widely used for the control and protection of medium and large steam turbines, heavy-duty gas turbines (single or two-shaft), and aircraft derivative gas turbines. As a core component of its power distribution system, the TCPSG1A ensures the continuous and stable operation of all processors, I/O modules, and communication networks in demanding industrial environments.
Key Functions of the DS200TCPSG1A
1. Multiple DC Voltage Outputs
The DS200TCPSG1A provides the various DC voltages required by the system, including:
+5V DC: Used for digital logic circuits and microprocessor core voltage.
±15V DC: Used for analog circuits, operational amplifiers, and sensor power.
+24V DC: Used for digital output modules, relays, solenoid valves, and other field device drives.
-24V DC: Required for certain specific interfaces or communication lines.
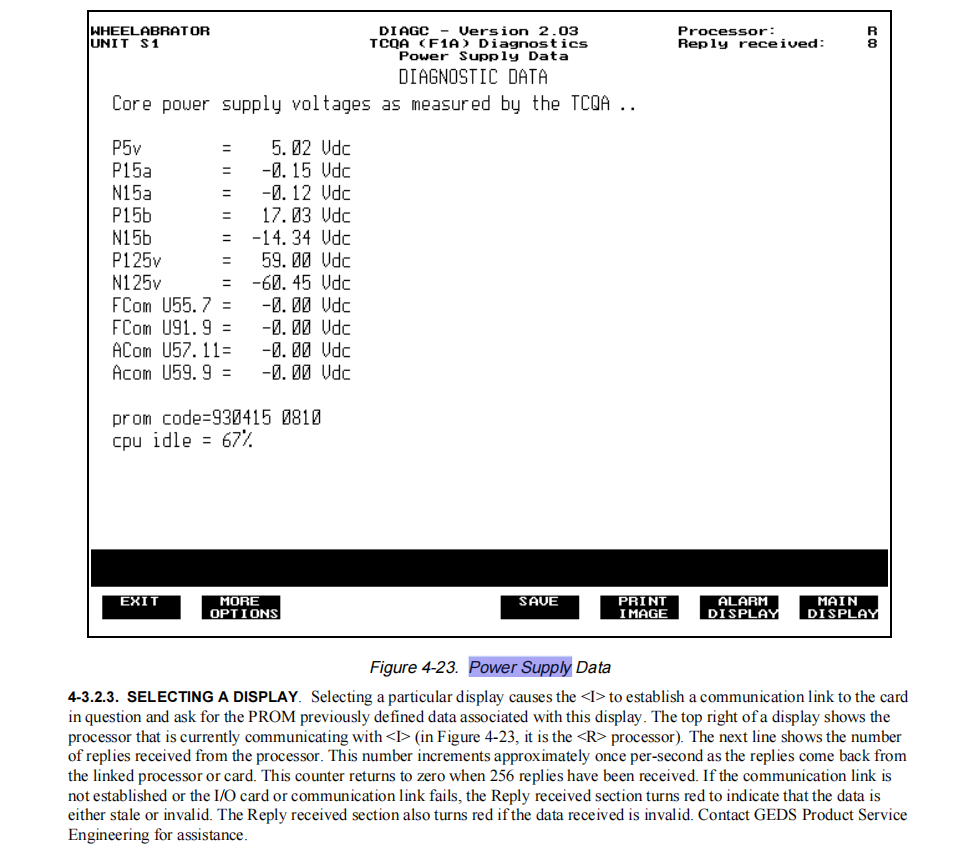
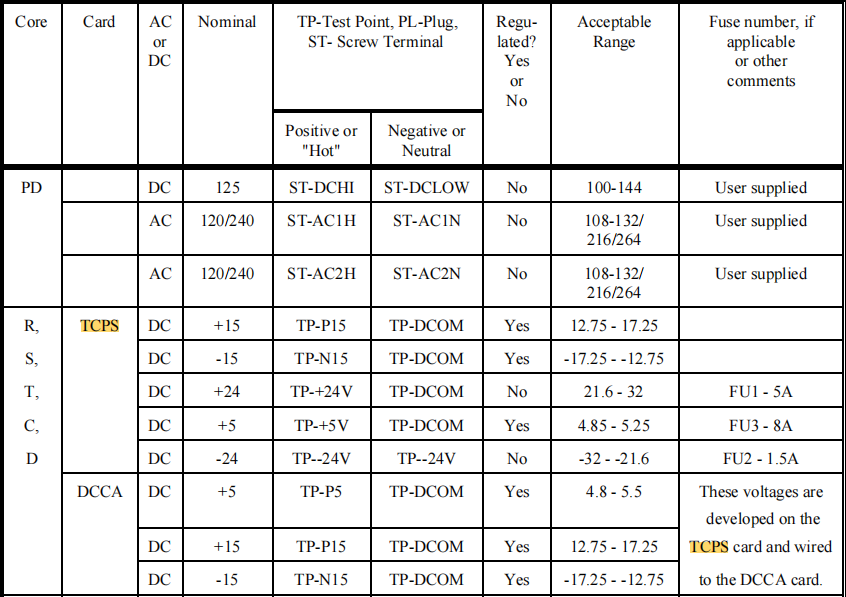
Each output is tightly regulated and filtered to ensure voltage fluctuations remain within allowable tolerances (e.g., +5V allowed range is 4.85–5.25V), preventing system malfunctions or damage due to power supply noise or load variations.
2. Power Status Monitoring and Diagnostics
The DS200TCPSG1A incorporates built-in voltage monitoring circuits that continuously check whether each output channel's voltage is normal. If over-voltage, under-voltage, or loss of voltage is detected, status information is sent via the IONET to the control processor (DCCA), triggering relevant diagnostic alarms. These alarms are displayed on the operator interface (<I>), alerting maintenance personnel for timely action.
3. Support for Online Maintenance and Hot-Swapping
In a Triple Modular Redundant (TMR) configuration, each control core (<R>, <S>, <T>) is equipped with an independent DS200TCPSG1A power module. If one power module fails, the system can continue operating using the remaining two power supplies, allowing the faulty module to be replaced without shutting down the turbine, significantly enhancing system availability.
4. Overcurrent and Short-Circuit Protection
Each output channel is equipped with fuses (e.g., FU1, FU2, FU3) or electronic current-limiting protection to prevent damage to the power module or backplane circuits caused by external device short circuits or overloads. The maintenance manual details the fuse ratings and replacement specifications (see Chapter 7).
5. Power Redundancy and Load Sharing
In a TMR system, the three power supplies operate in parallel, providing not only redundancy but also sharing the load, which reduces the operational stress on any single supply and extends its service life.
Working Principle of the DS200TCPSG1A
1. Power Input and Primary Processing
The input power for the DS200TCPSG1A typically comes from the control panel's Power Distribution core (<PD>). The input can be:
The input power first passes through input filtering and surge suppression circuits to prevent grid interference or lightning strikes. It then enters a switching or linear regulator circuit for initial step-down and rectification.
2. DC-DC Conversion and Regulation
The DS200TCPSG1A utilizes high-frequency switching power supply technology (or linear regulation technology, depending on the model) to convert the input voltage to the required low-voltage DC outputs. The switching power supply uses PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) to control the conduction time of MOSFETs or IGBTs, adjusting the output voltage. A feedback loop (typically implemented via optocouplers or error amplifiers) ensures precise voltage regulation.
For example:
+5V Output: Typically generated by a dedicated Buck converter for digital circuits.
±15V Output: May be generated by a flyback or push-pull converter for analog circuits.
+24V Output: Often generated by a Boost or Buck-Boost circuit for high-power output modules.
3. Voltage Feedback and Adjustment
Each output has a sampling resistor voltage divider network that feeds the output voltage back to a control IC (e.g., TL431, SG3525). The control IC adjusts the PWM duty cycle based on the difference between the set value and the actual value, implementing closed-loop control to keep the output voltage stable near its rated value.
4. Protection Mechanisms
Overcurrent Protection: Output current is monitored via current-sense resistors or transformers. If the current exceeds a set threshold, the protection circuit limits the output or shuts down the supply.
Overvoltage Protection: Implemented using Zener diodes or dedicated OVP chips to prevent abnormal output voltage spikes.
Thermal Protection: A temperature sensor inside the power module automatically reduces the load or shuts down the supply if the temperature exceeds safe limits.
5. Status Communication
The DS200TCPSG1A communicates with the main control processor (DCCA) via the IONET. The DCCA periodically polls the status word of each power module (including voltage normal/abnormal status, temperature, load status, etc.) and aggregates this information for monitoring on the <I>. Using the DIAGC (Diagnostic Data Display) tool, maintenance personnel can view the specific voltage values of each power supply in real-time (see Figure 4-23), facilitating troubleshooting.
6. Integration with Other System Modules
The DS200TCPSG1A not only powers the local core but also supplies other cards within the same core (e.g., TCDA, TCEA, LCC) via the backplane power bus. In the TMR system, the three power systems are completely independent to avoid common-cause failures. Furthermore, the fault status of a power module participates in the system's voting logic, ensuring that a single power supply failure does not affect overall control decisions.