The IS220PTURH1B is a Turbine Specific Primary Trip I/O Pack used in GE's Mark VIe and Mark VIeS control systems. It is a model within the PTUR series, containing a functionally compatible BPPC processor board that requires ControlST software suite V04.07 or later. This module serves as the electrical interface between turbine control terminal boards (e.g., TTURH1C, TRPAH1A, STURHxA) and one or two I/O Ethernet networks, acting as a core component for implementing critical turbine protection and control functions.
The IS220PTURH1B is specifically designed to handle signals essential for the safe and stable operation of steam and gas turbines, including speed monitoring, automatic synchronization (sync), shaft voltage/current monitoring, and (when used with the TRPG terminal board) flame detection. Its ultimate goal is to reliably drive the main breaker and primary trip solenoids, ensuring rapid unit shutdown in dangerous conditions such as overspeed. The module supports both Simplex and Triple Modular Redundant (TMR) system configurations, providing a highly reliable primary protection layer for various turbine applications.
Core Functional Description
The IS220PTURH1B integrates multiple signal processing functions into a comprehensive turbine primary protection platform.
Four Speed Sensor Inputs
Speed: For normal single-shaft turbines.
Speed_High: Provides an extended speed range above the standard type.
Speed_HSNG: Used to compensate for inconsistent tooth spacing on the speed wheel, using a tooth mapping algorithm to remove periodic errors from speed measurements.
Speed_LM: Designed for LM series gas turbines.
Flow: For flow divider fuel flow measurements.
Interface Type: Provides 4 channels for connecting passive magnetic speed pickups.
Frequency Range: Supports a wide pulse rate input range from 2 Hz to 20,000 Hz, enabling accurate measurement from 2 RPM turning gear speed (to determine if the rotor is stopped) to overspeed signals far above the rated speed.
Signal Conversion: Internal circuits convert pulse frequency signals into digital speed values.
Pulse Rate Type Configuration: The application type can be flexibly configured via the PRType parameter:
Generator and Bus Voltage Inputs (Automatic Synchronization)
Input Signals: Receives generator voltage and bus voltage signals from external Potential Transformers (PTs), nominal 115 V RMS.
Core Function: These inputs are used for the automatic synchronization function, allowing the generator to precisely match the voltage, frequency, and phase of the system bus before closing the breaker.
Measurement Accuracy: Frequency measurement accuracy is 0.05% over the 45-66 Hz range; phase difference measurement accuracy is better than ±1°.
Shaft Voltage and Shaft Current Monitoring
AC Test: Applies a 2 kHz test voltage to verify the integrity of the measuring circuit.
DC Test: Applies a 5 V DC source to test the continuity of the external circuit (including brushes, shaft, and interconnecting wires). Resistance readings above the BrushLimit setting indicate a potential fault.
Purpose: To monitor bearing potential damage caused by electrical current flow, which can stem from static electricity (e.g., water droplets from last-stage buckets in steam turbines), AC ripple on the generator field, or generator magnetic circuit dissymmetries.
Monitoring Content:
Test Functions:
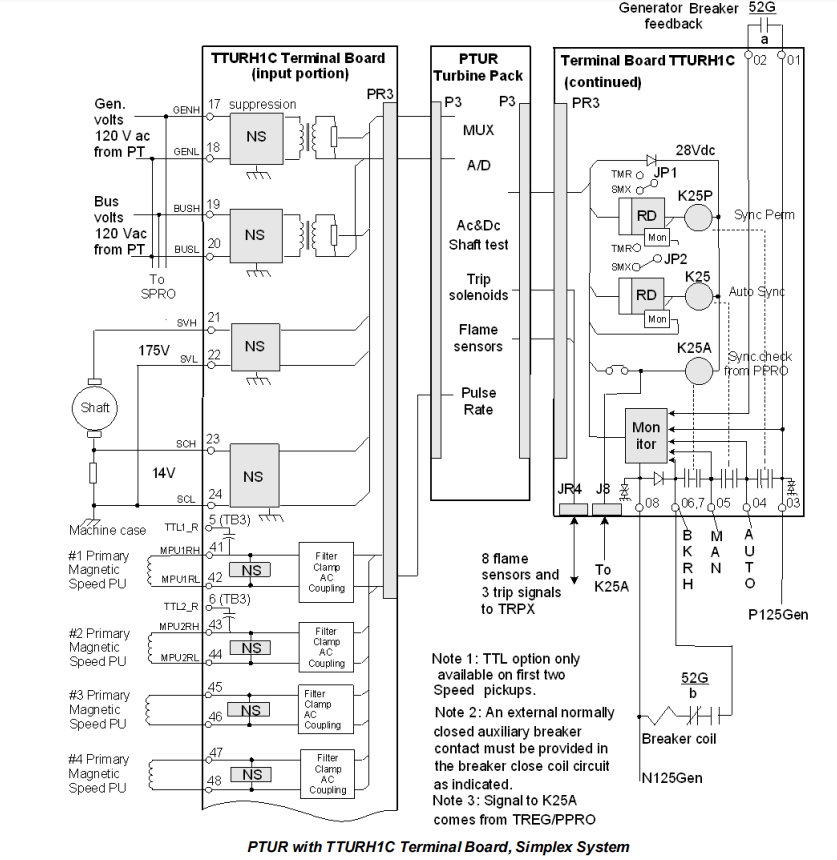
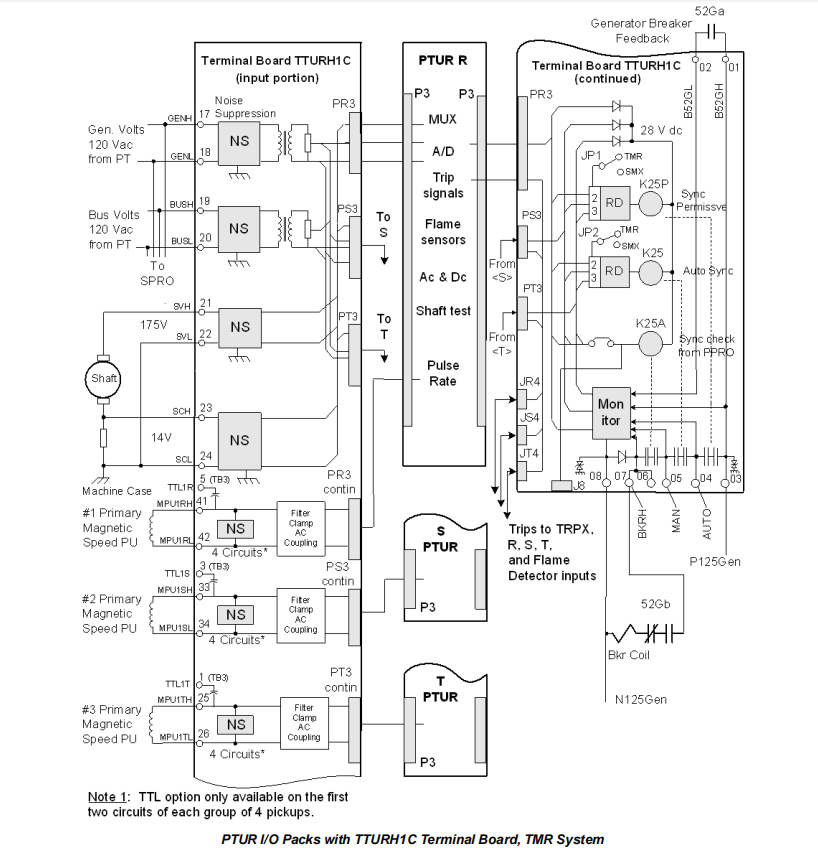
Flame Detector Inputs (with TRPG)
When used with the TRPG primary trip terminal board, the PTURH1B can monitor signals from eight flame detectors.
Operating Principle: With no flame, the detector charges to the supply voltage. The presence of flame causes the detector to charge to a level and then discharge through the TRPG. Higher flame intensity increases the discharge frequency (0-1000 pulses/sec). The PTUR converts these discharge energies into voltage pulses and counts them.
Output Functions
Primary Trip Solenoid Interface: Drives trip solenoids connected to TRPx series trip terminal boards (up to 3), ultimately triggering the turbine's emergency trip system.
Automatic Synchronization Control: Issues precise close commands to the main breaker (52G) closing coil by controlling the K25 (Auto Sync) relay on the TTURH1C terminal board.
Synchronizing Permissive: Provides sequence permission for generator synchronization by controlling the K25P relay.
Diagnostics and Status Monitoring
The module provides comprehensive self-diagnostics, including power supply monitoring, hardware checks, communication status, and feedback monitoring of critical relays and sensors.
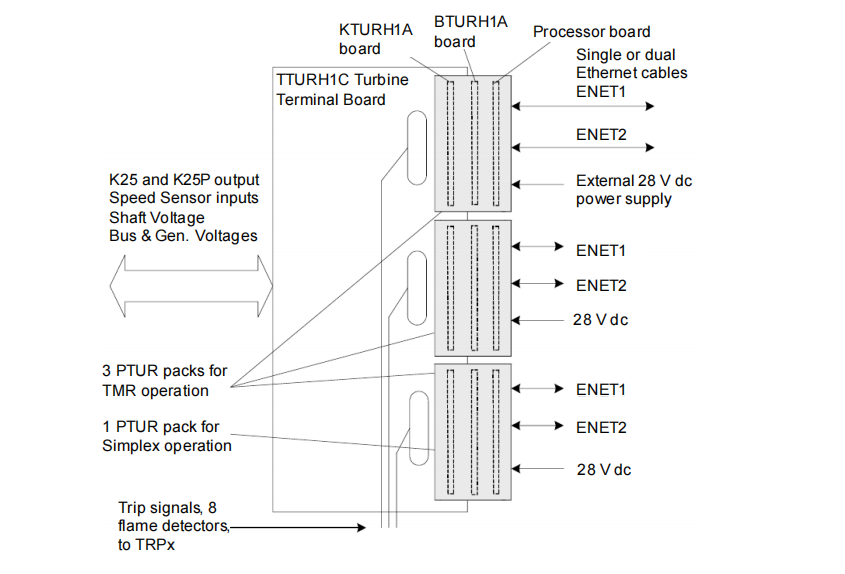
Hardware Architecture and Operating Principles
(A) Hardware Composition
The IS220PTURH1B module consists of:
BPPC Processor Board: The common processor core for distributed I/O packs, handling communication, logic processing, and data processing.
Application-Specific Board: Contains dedicated circuitry for processing turbine-specific signals (e.g., speed, voltage).
Analog Acquisition Daughterboard: Responsible for high-precision acquisition of analog signals like voltages and shaft monitoring signals.
Connectors:
Bottom DC-62 pin connector: Plugs directly into the corresponding terminal board (TTUR, STUR, TRPA), transmitting all I/O signals.
RJ-45 Ethernet Ports (ENET1, ENET2): For communication with the Mark VIe controller, supporting single or dual network redundancy.
3-pin power input: External 28V DC power supply.
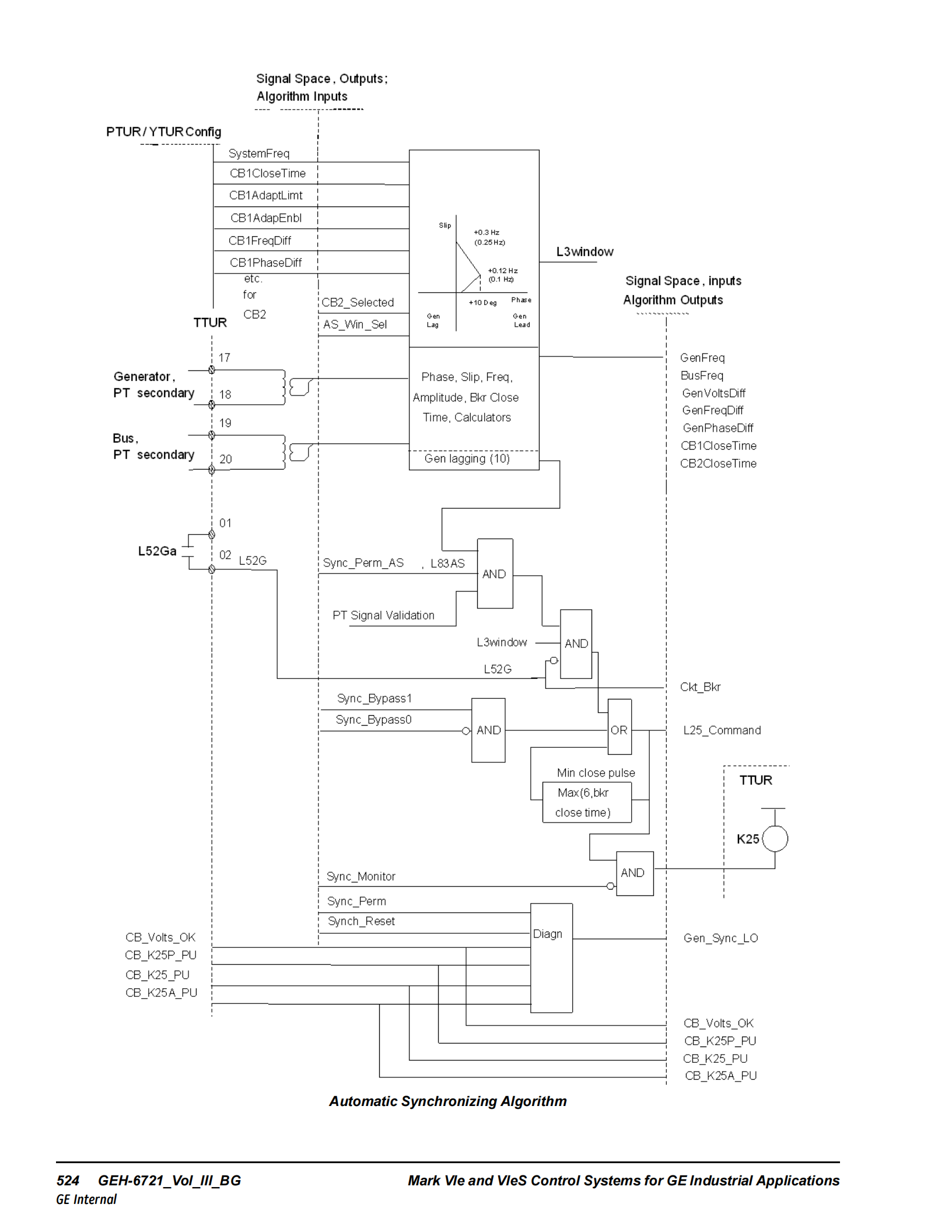
(B) Automatic Synchronizing System Principles
This is one of the most complex and core functions of the IS220PTURH1B, aiming to close the generator breaker at the optimal moment (near zero phase difference) for a smooth connection to the grid.
Signal Acquisition and Calculation:
The IS220PTURH1B continuously monitors generator voltage (V_Gen) and bus voltage (V_Bus).
It precisely calculates the phase difference (GenPhaseDiff), slip (GenFreqDiff, frequency difference), and acceleration between them using a zero-voltage crossing technique.
Slip: Positive when the generator frequency is higher than the bus frequency. Phase: Positive when the generator is leading the bus.
Close Decision and Prediction:
The auto sync algorithm does not issue the close command precisely at the zero phase difference instant but must predict the breaker's operating time.
Based on the current phase, current slip, current acceleration, and the configured Breaker Close Time (CBxCloseTime), the algorithm calculates a projected closing lead time.
The close command is issued if the generator is currently lagging (negative phase difference) and has been lagging for at least the last 10 consecutive cycles, AND the algorithm anticipates it will be leading at the actual moment of breaker closure. This strategy ensures minimal phase difference at the instant of closure.
Relay Coordination:
Closing the generator breaker requires three conditions met simultaneously, controlled by three relays:
K25P (Sync Permissive Relay): Driven directly by the controller application code. Checks if the turbine is in the correct sequence state for synchronization.
K25 (Auto Sync Relay): Driven by the auto sync algorithm inside the PTURH1B. Activates when voltage, frequency, and phase conditions are met and closure is predicted accurately.
K25A (Sync Check Relay): Located on TTUR, but driven by the sync check algorithm in the PPRO or YPRO I/O module (based on 2-out-of-3 logic). Serves as an independent backup check, ensuring the phase or slip is within a permissible window.
The breaker close circuit is completed only if K25A picks up first (to prevent its interference with the optimization), followed by K25 and K25P.
Adaptive Control:
The algorithm features self-adaptive control of the breaker close time. It measures the actual breaker close time using feedback from the 52G/a auxiliary contact after each closure and compares it to the setpoint.
It then automatically adjusts the CBxCloseTime parameter by increments of one cycle (16.6/20 ms) per closure to bring it closer to the actual value, continuously improving closing accuracy. This adjustment is limited by the configurable CBxAdaptLimit parameter.
Operating Modes:
Off: Synchronizing is disabled.
Manual: The operator initiates the close command, but it is still subject to the K25A contacts.
Auto: The system automatically matches voltage and speed, then closes the breaker at the right time.
Monitor: Identical to Auto mode, but blocks the actual output of the K25 relay, used for testing and verifying system performance without actually closing the breaker.
(C) Fast Overspeed Protection Principles
For applications requiring extremely fast response, the IS220PTURH1B can enable built-in fast overspeed trip algorithms. The trip logic is executed directly within the PTUR, bypassing the controller, resulting in a trip time of 30 ms or less.
PR_Single Algorithm:
Application: Primarily used for LM gas turbines, providing redundancy.
Principle: Two redundant speed sensor signals are split to two redundant PTURs. Each PTUR independently processes its own speed signals (PulseRate1 to PulseRate4).
Protection Types: Each speed channel can have an independent overspeed setpoint (PRxSetpoint). Also provides acceleration trip protection (AccATrip, AccBTrip) to protect against rapid rotor acceleration.
PR_Max Algorithm:
Application: A single PTUR is connected to two redundant speed sensors.
Principle: The algorithm uses the maximum value of two speed signals (MAX(PR1, PR2) and MAX(PR3, PR4)) for decision-making.
Protection Types: Besides overspeed and acceleration protection, it also provides deceleration trip (DecelTrip) protection (against shaft failure) and speed difference trip (FastDiffTrip). If one sensor fails, the other can still provide protection, avoiding nuisance trips.
(D) Shaft Voltage/Current Monitoring Principles
Installation, Configuration, and Diagnostics
Installation:
Plug the IS220PTURH1B module directly into the connectors of the mounted terminal board (TTUR, STUR, TRPA).
Mechanically secure the I/O pack using the threaded studs adjacent to the Ethernet ports and a specific mounting bracket, ensuring no right-angle force is applied to the DC-62 pin connector.
Connect one or two Ethernet cables and the 28V DC power supply.
Configuration (Using ToolboxST Software):
Pulse Rate Parameters: Set PRType, PRScale (pulses per revolution), TeethPerRev (teeth on speed wheel), etc.
Auto Sync Parameters: Configure CBxCloseTime (breaker closing time), CBxAdaptLimit (adaptive limit), etc.
Fast Trip Parameters: Select TripType (PR_Single or PR_Max) and set corresponding overspeed, acceleration, deceleration setpoints.
System Limits: Set alarm and trip limits for various signals.
Diagnostics and LED Indicators:
K25: Indicates a command to energize the auto sync relay.
K25P: Indicates a command to energize the sync permissive relay.
DCT: Indicates DC Test is enabled.
K1, K2, K3: Indicates a command to energize the corresponding trip relay.
The PTURH1B performs power-up self-tests and continuous hardware monitoring.
LEDs on the module faceplate provide key status indications:
Detailed diagnostic alarms, such as sync relay faults, breaker adaptive adjustment limits exceeded, and hardware mismatches, can be viewed in ToolboxST, guiding troubleshooting steps.