The CV214 velocity transducer is a high-performance vibration measurement device from VM Sensing Systems, specifically designed for low-frequency vibration monitoring. Suitable for various industrial environments, it excels particularly in monitoring vibrations on slow-speed rotating machinery. Its robust construction, moderate operating temperature range, and self-generating nature make it an ideal choice for critical equipment such as hydroelectric and steam turbines, especially suited for medium-to-low temperature applications.
Features & Benefits
1. Wide Frequency Response & High Sensitivity
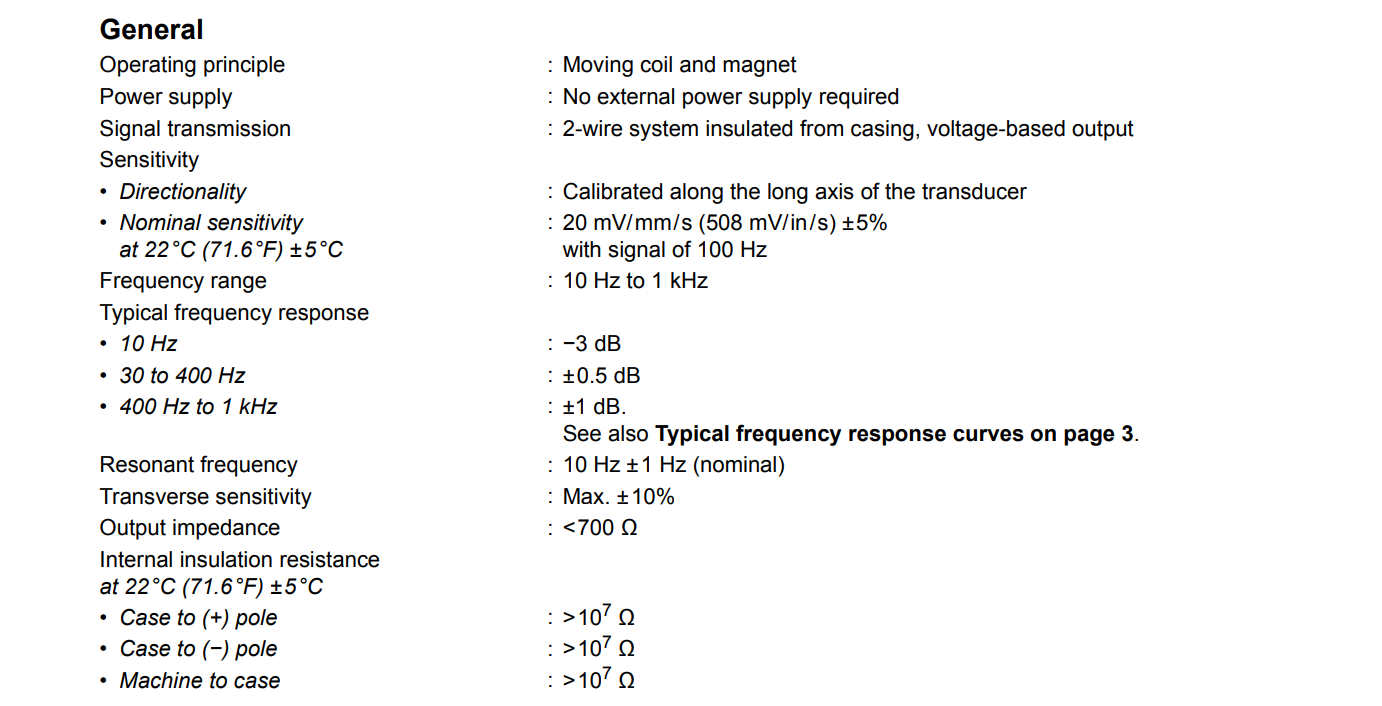
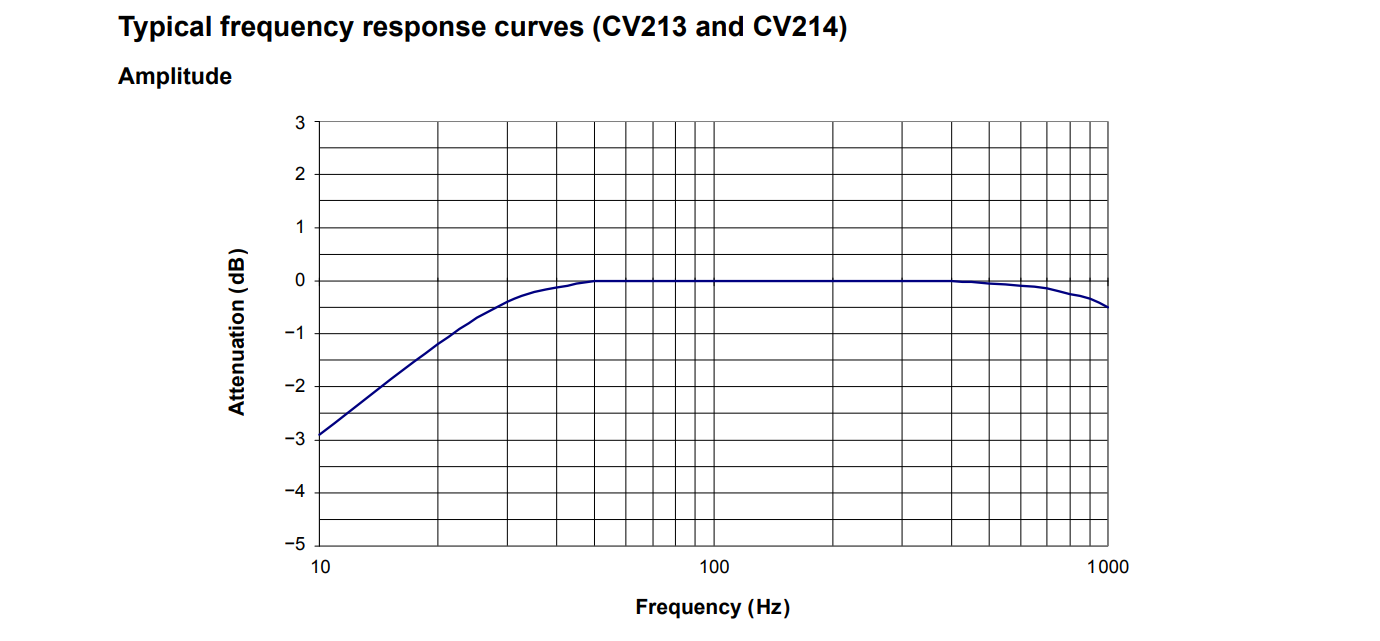
The CV214 offers a broad frequency response range from 10 Hz to 1 kHz, making it particularly adept at capturing low-frequency vibration signals. Its nominal sensitivity is 20 mV/mm/s (508 mV/in/s), with a tolerance of ±5% at 22°C, ensuring accurate and stable vibration data even on slow-speed machines. The transducer's frequency response deviation is only ±0.5 dB within the 30–400 Hz range and ±1 dB within the 400 Hz–1 kHz range, with a -3 dB point at 10 Hz, ensuring excellent linear characteristics.
2. Self-Generating Operation (No Power Required)
Operating on the electromagnetic induction principle, this transducer requires no external power supply. It generates a voltage output signal proportional to vibration velocity. This feature makes it especially suitable for portable measurement systems or remote monitoring applications where power availability is limited or undesirable. The low output impedance (<700 Ω) ensures a high signal-to-noise ratio and strong noise immunity during signal transmission.
3. Good Environmental Durability
The CV214 operates reliably in temperatures from -29°C to 121°C (-20°F to 250°F). It boasts an IP64 protection rating, making it resistant to dust and moisture ingress, and is suitable for damp, corrosive, or dusty industrial environments. Its internal insulation resistance is greater than 10⁷ Ω at ambient temperature, ensuring electrical safety and stability.
4. Certifications for Hazardous Areas
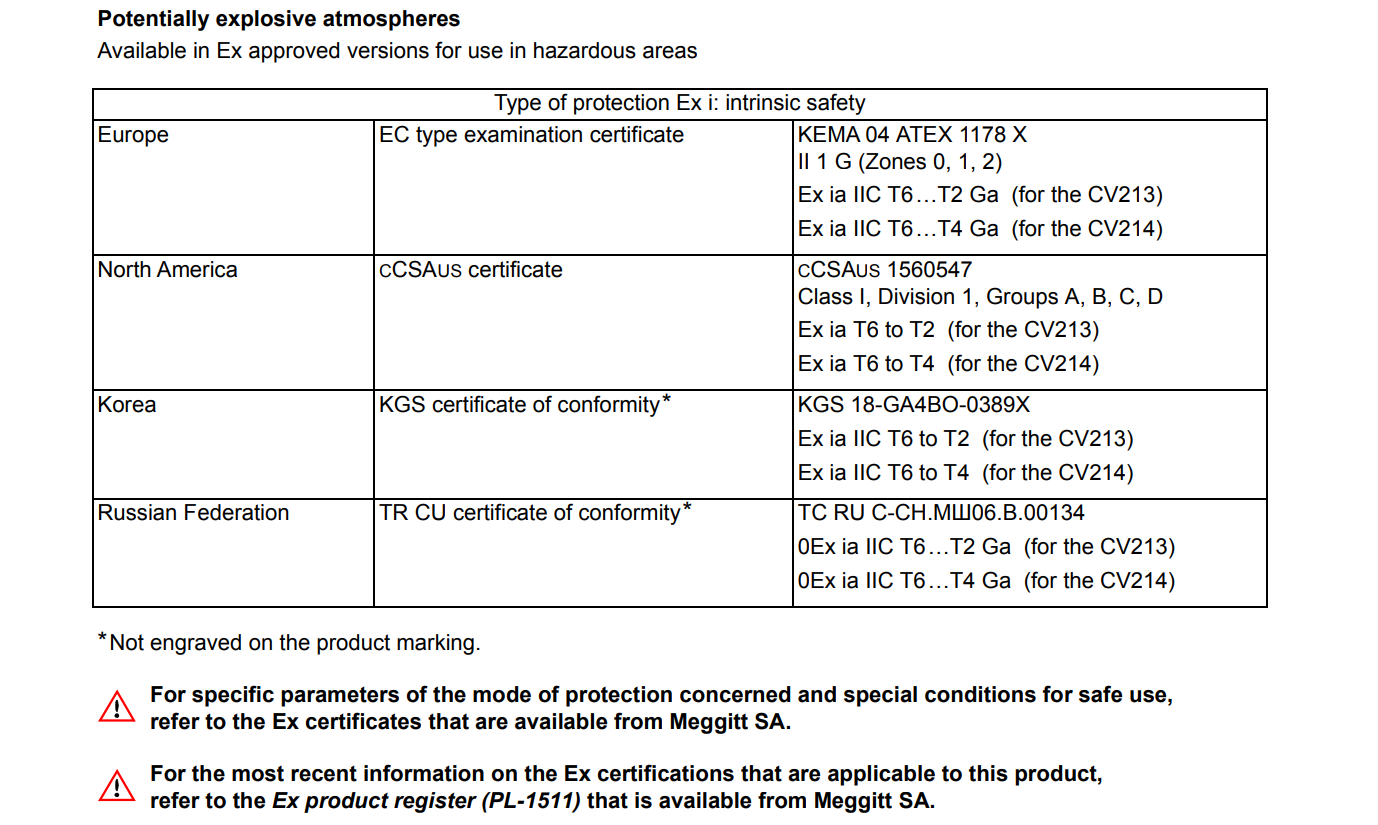
The transducer is certified for use in potentially explosive atmospheres by various international standards, including European ATEX, North American cCSAus, Korean KGS, and Russian TR CU. It is approved for safe operation in hazardous areas (e.g., Zone 0/1/2 or Division 1). Its explosion-proof designation is Ex ia IIC T6…T4 Ga, suitable for the corresponding temperature classes in hazardous environments.
5. Rugged Mechanical Construction
The sensor housing is constructed from anodized Anticorodal 100 aluminum alloy. The mounting foot is made of Rylon®, a high-performance thermoplastic, and the mounting screw is stainless steel (AISI 304). This combination ensures overall durability and corrosion resistance. The transducer can withstand shock acceleration of 50 g peak (half-sine wave, 1 ms duration).
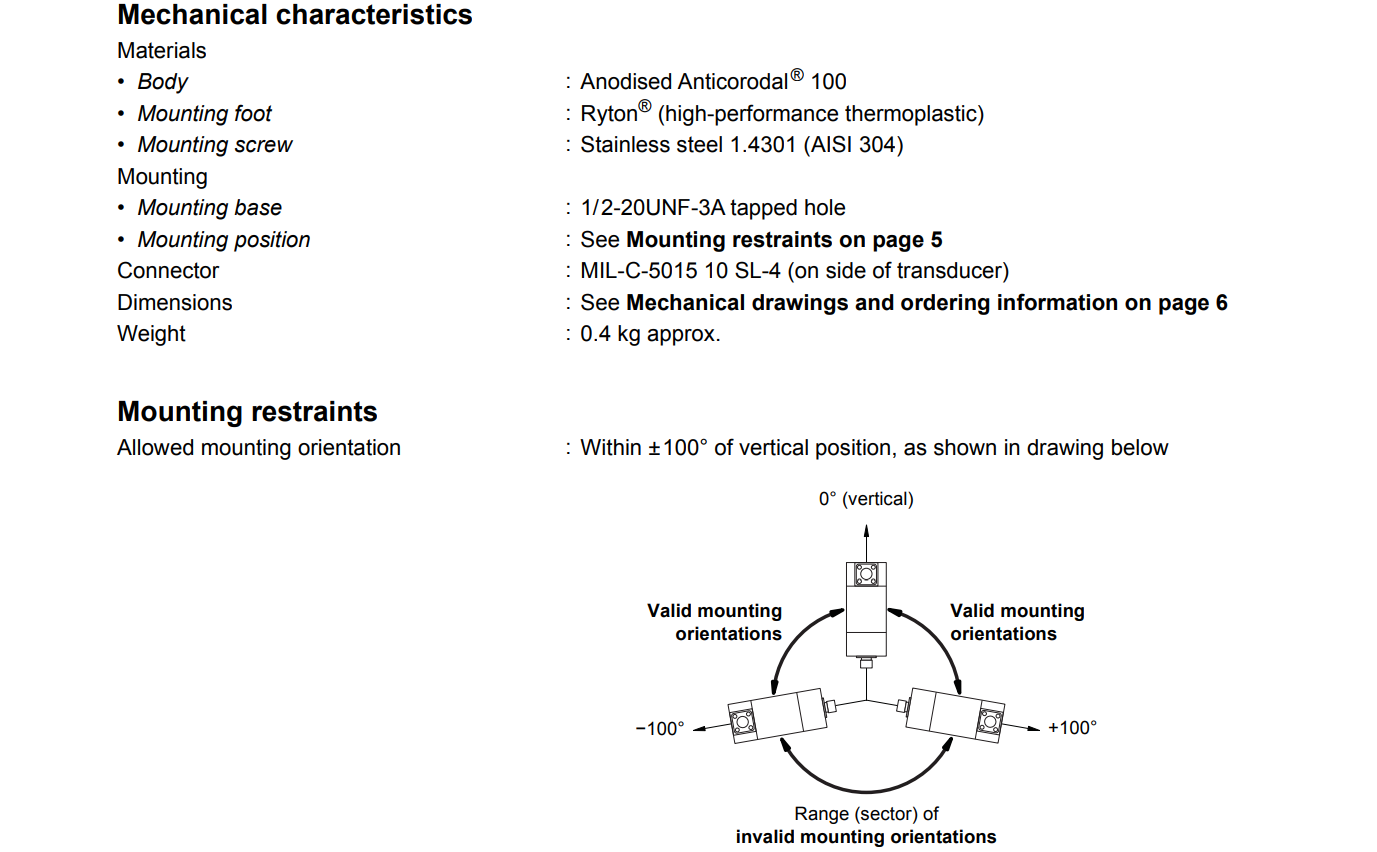
6. Flexible Mounting Options
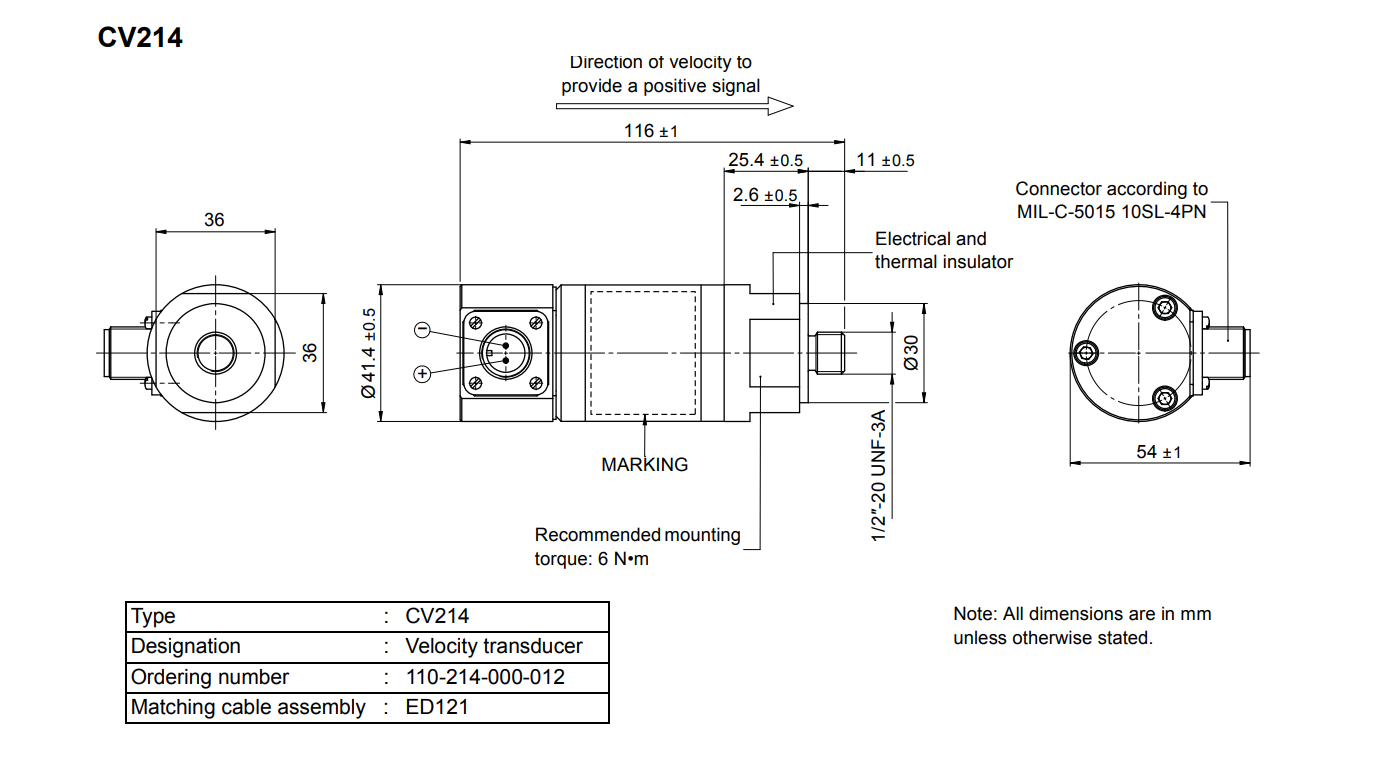
The CV214 can be mounted within ±100° of the vertical position, accommodating various mechanical layouts. The recommended mounting torque is 6 N·m, ensuring secure installation without damaging the equipment. The mounting base features a 1/2-20UNF-3A tapped hole, complying with standard mounting specifications.
7. No Signal Conditioner Required
The transducer provides a voltage output signal that can be connected directly to monitoring electronics, eliminating the need for and cost associated with an additional signal conditioning module, thus simplifying system integration. Signal transmission uses a 2-wire system insulated from the casing, enhancing safety and reliability.
8. Low Transverse Sensitivity
The maximum transverse sensitivity is ±10%, ensuring the transducer is primarily sensitive to axial vibration. This reduces the influence of cross-axis sensitivity on measurement results and improves the accuracy of the data.
Working Principle
The CV214 velocity transducer operates based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. Its core sensing element consists of a moving coil and a fixed permanent magnet. When the transducer is mounted on a vibrating structure, the vibration causes the coil to move relative to the magnet. According to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, this movement induces an electromotive force (voltage) in the coil, which is directly proportional to the vibration velocity.
Detailed Operational Mechanism:
Vibration Transfer: Vibration is transferred from the machine surface to the sensor's internal mechanical structure via its mounting base.
Inertial System Movement: The internal inertial system (including the coil) moves relative to the housing (and the magnet) under the effect of vibration. The coil cuts the magnetic flux lines of the fixed magnetic field generated by the permanent magnet.
EMF Generation: Cutting the magnetic flux lines induces an electromotive force (EMF) in the coil. According to Faraday's law, the magnitude of the EMF is proportional to the rate at which the coil cuts the flux lines, i.e., proportional to the vibration velocity.
Signal Output: The generated voltage signal is transmitted to the monitoring equipment via the side-mounted MIL-C-5015 10 SL-4 type military-standard connector and matching cable. The signal amplitude directly corresponds to the vibration velocity.
Frequency Response: The mechanical structure (mass-spring-damper system) of the sensor determines its frequency characteristics. Its natural frequency is designed to be 10 Hz ±1 Hz. Within a certain range above the natural frequency (10 Hz - 1 kHz), the output signal linearly follows the change in vibration velocity. The typical amplitude-frequency response is: -3 dB at 10 Hz, ±0.5 dB within 30–400 Hz, and ±1 dB within 400 Hz–1 kHz.
Advantages:
Self-Powered: Requires no external power supply, simplifies system architecture, eliminates noise from power lines, and is ideal for hazardous environments or remote locations.
High Reliability: As a passive device, it has fewer moving parts and electronic components. Its simple structure is robust and durable, offering a long mean time between failures (MTBF).
High Signal-to-Noise Ratio: The output signal amplitude is relatively large (20 mV/mm/s), and the low output impedance (<700 Ω) provides strong immunity to electromagnetic interference, making it suitable for long-distance transmission.
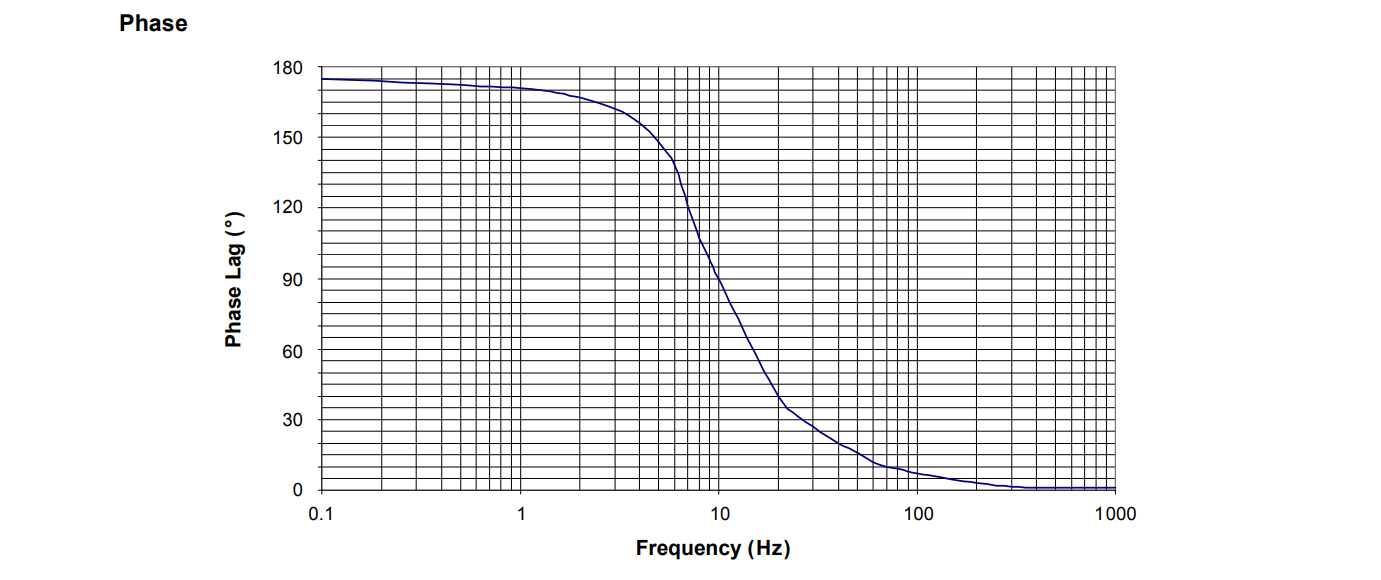
Stable Phase Response: Consistent phase response across the frequency band suits phase-sensitive diagnostic systems, facilitating precise phase analysis.
Direct Velocity Measurement: Vibration velocity is a parameter commonly used by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) to assess the severity of machine vibration. The CV214 directly outputs a signal proportional to velocity, eliminating the need for integration or differentiation and avoiding the associated errors and phase shifts.
Applications
The CV214 is primarily used in the following fields:
Hydroelectric Generators: Monitoring vibration of turbines, generator bearings, and frames, particularly suitable for the damp environments of hydropower plants.
Steam Turbines: Suitable for vibration monitoring on critical components like intermediate and low-pressure casings, and bearing housings. Its temperature range covers the requirements of most steam turbine applications.
Slow-Speed Industrial Machinery: Such as fans, pumps, compressors, gearboxes, and large motors for routine vibration monitoring and protection.
Portable Vibration Measurement Systems: No power requirement facilitates easy temporary installation and spot checks on-site, making it an ideal tool for PdM (Predictive Maintenance) engineers.
Potentially Explosive Atmospheres: With its comprehensive explosion-proof certifications, it can be used in hazardous areas with flammable gases or dust in industries such as oil, gas, and chemicals.
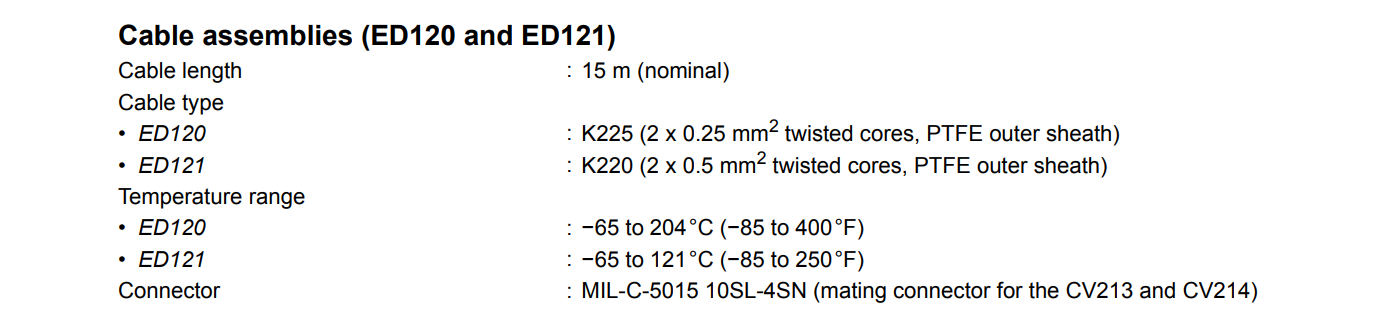
Matching Cable & Installation Advice
The CV214 is designed for use with the dedicated ED121 cable assembly. This cable has a nominal length of 15 meters, features twisted and shielded pairs (2 × 0.5 mm² stranded cores), and has a PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) outer sheath, offering excellent chemical resistance and high-temperature properties. Its operating temperature range is -65°C to 121°C. The cable is terminated with a MIL-C-5015 10SL-4SN connector, mating perfectly with the sensor's connector.
In extremely harsh industrial environments (e.g., with risks of high temperature, abrasion, or crushing), it is recommended to protect the cable assembly further with a flexible metal conduit (flexible sheath) for mechanical protection.
During installation, ensure the sensor mounting surface is clean and flat to achieve optimal frequency response and measurement accuracy. Tighten the mounting screw to the recommended torque of 6 N·m to ensure sufficient mounting stiffness, while avoiding over-tightening which could damage the sensor or the equipment threads.
Key Specifications Summary
Operating Principle: Moving coil electromagnetic induction
Sensitivity: 20 mV/mm/s (508 mV/in/s) ±5% (@100 Hz, 22°C)
Frequency Range: 10 Hz – 1 kHz (-3 dB @10 Hz)
Resonant Frequency: 10 Hz ±1 Hz
Transverse Sensitivity: Max. ±10%
Output Impedance: <700 Ω
Operating Temperature: -29°C to 121°C (-20°F to 250°F)
Storage Temperature: -40°C to 100°C (-40°F to 212°F)
Protection Rating: IP64 (IEC 60529)
Shock Resistance: 50 g peak (half-sine wave, 1 ms duration)
Connector: MIL-C-5015 10 SL-4 (side-mounted)
Mounting Torque: 6 N·m
Weight: approx. 0.4 kg
Explosion-Proof Certifications: ATEX, cCSAus, KGS, TR CU (see Specifications for more details)